17 Attaches the correct amino acid to its transfer RNA. 2 A molecule that binds to a specific codon and specific amino acid simultaneously.

At least two classes of.
Attaches the correct amino acid to its transfer rna. Attaches the correct amino acid to its transfer RNA. As we know tRNA is an adapter molecule that carries amino acids in an activated form to ribosomes for protein synthesis. There is at least 1 tRNA molecule for each of the 20 amino acids.
It adopts a folding structure with internal base pairing and is about 75 nucleotides long. 17 Attaches the correct amino acid to its transfer RNAB 18 Provides the energy from BIO 141 at Northern Virginia Community College. 2 A molecule that binds to a specific codon and specific amino acid simultaneously.
3 Attaches the correct amino acid to its transfer RNA. 4 Provides the energy needed for synthesis reactions. 5 Produced in the nucleus this molecule specifies the exact sequence of amino acids of the.
The attachment of an amino acid to the tRNA is catalyzed by an enzyme known as aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. The enzyme has high specificity and is usually very accurate in attaching the correct amino acid to a specific RNA molecule. At least two classes of.
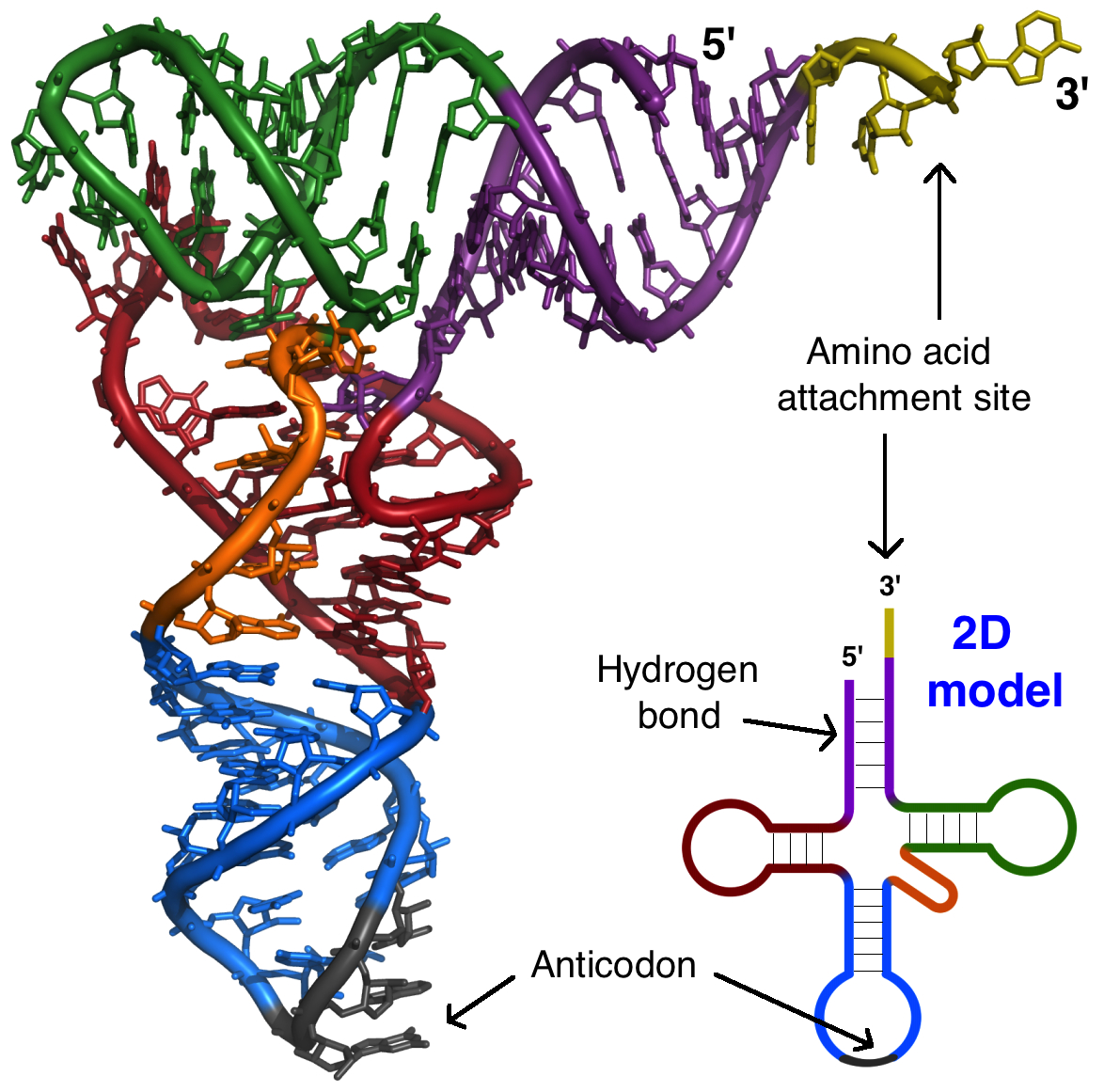
TRNA transfer RNA attaches to the mRNA by the codon and anticodonEach tRNA carries an amino acid that corresponds to the codon on the mRNA. This is how the correct amino acid. Transfer RNA tRNA Each tRNA molecule has two important areas.
A trinucleotide region called the anticodon and a region for attaching a specific amino acid. During translation each time an amino acid is added to the growing chain a tRNA molecule forms base pairs with its complementary sequence on the messenger RNA mRNA molecule ensuring that the appropriate amino acid is inserted into the. 16 A molecule that binds to a specific codon and specific amino acid simultaneously.
17 Attaches the correct amino acid to its transfer RNA. 18 Provides the energy needed for synthesis reactions. 19 Produced in the nucleus this molecule specifies the exact sequence of amino acids.
Transfer RNA or tRNA has the important job of making sure the correct amino acids are put into the polypeptide chain in the correct order during the process of translation. It is a highly folded structure that holds an amino acid on one end and has what is called an anticodon on the other end. The enzyme that attaches the amino acid to the transfer RNA ribonucleic acid is Aminoacyl transferase synthetase.
It aids in the binding of the correct amino acid based on the codons that code. An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase aaRS or ARS also called tRNA-ligase is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA.
The attachment of an amino acid to its tRNA is called amino acylation or charging. The amino acid is covalently attached to the end of the acceptor arm of the tRNA which always ends with the base sequence 5 CCA 3. A bond forms between the carboxyl group of the amino acid and the 3-hydroxyl of the terminal adenine of the acceptor arm.