Industrial robots commonly have four or six axes. Hydraulic Drive It is associated with larger robots such as Unimate 2000 series.
When arms of a robot move in the XYZ rectangular coordinate system it is known as a Cartesian robot.
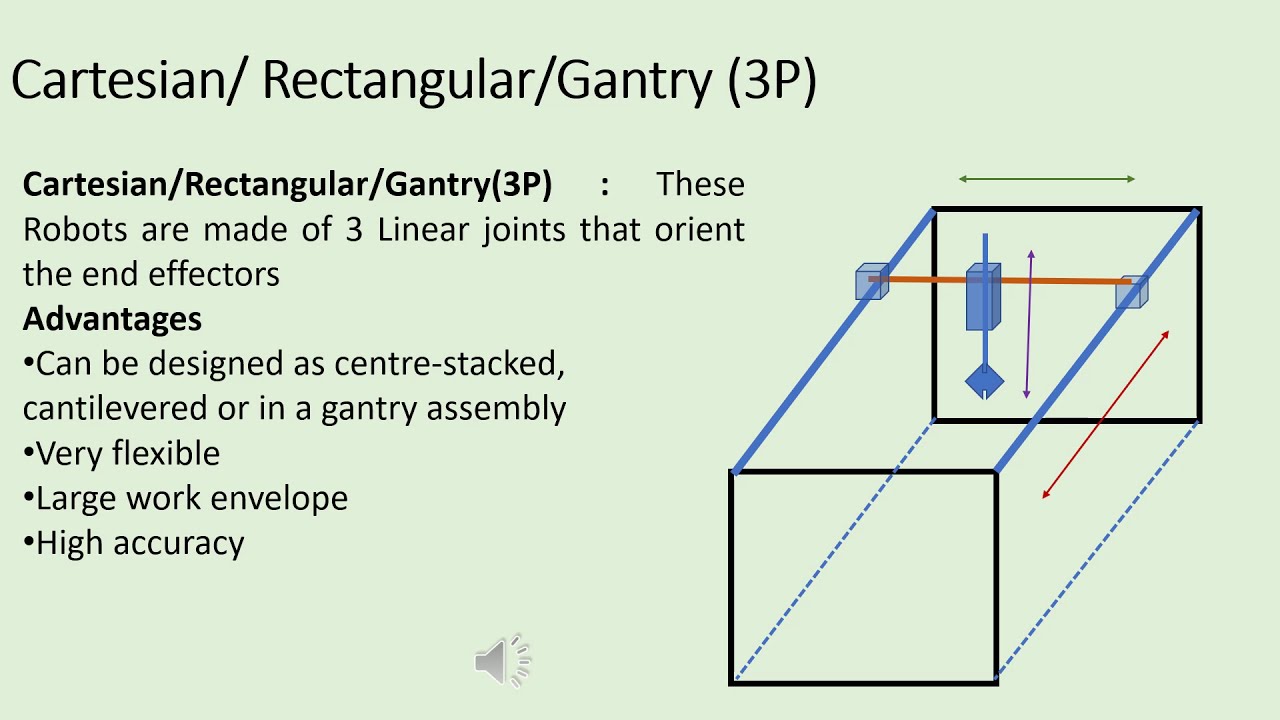
Classification of robots based on coordinate system. Classification of robots based on the workspace geometry It is the most commonly used robot type in the industries. It is popular because it is easy to use and program. In this robot the Kinetic structure of the arm is made up of three mutually perpendicular Prismatic joints.
Robot targets and positions are located by measurements along the axes of coordinate systems. A robot uses several coordinate systems each suitable for specific types of jogging or programming. The Robots are mostly divided into four major configurations based on their appearances sizes etc.
Cartesian robot consists of three prismatic joints and axes are concurrent with a Cartesian coordinate system. SCARA Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm robot is included with two parallel rotary joints to provide compliance in a plane. Robot whose arm has three prismatic joints and whose axes are coincident with a cartesian coordinate system SCARA robot.
A robot which has two parallel rotary joints to provide compliance in a plane Articulated robot. A robot whose arm has at least three rotary joints. Similarly Robots can be classified based on their coordinate systems ie.
Based on reachable coordinates of a point on the end-effector. When arms of a robot move in the XYZ rectangular coordinate system it is known as a Cartesian robot. It needs a large volume to operate and has a rigid structure.
A cartesian coordinate robot also called linear robot is an industrial robot whose three principal axis of control are linear ie. They move in a straight line rather than rotate and are at right angles to each otherThe three sliding joints correspond to moving the. Industrial robots commonly have four or six axes.
Cartesian - These are also called rectilinear or gantry robots. Cartesian robots have three linear joints that use the Cartesian coordinate system X Y and Z. They also may have an attached wrist to allow for rotational movement.
TYPES OF ROBOT There are five types of robots which are. Cartesian robot Cylindrical Spherical ArticulatedAnthropomorphic robot SCARA 15. CARTESIAN ROBOT 3L A Cartesian robot also known as a Cartesian coordinate robot is a common type of industrial robot.
In controlled-path robots the control equipment can generate paths of different geometry such as straight lines circles and interpolated curves with a high degree of accuracy. Good accuracy can be obtained at any point along the specified path. Hydraulic Drive It is associated with larger robots such as Unimate 2000 series.
Generally provide great speed and strength. Requires electric drives to pump oil. Can be used to actuate rotary as well as linear joints.
Has problem of oil leakage. Bulky and adds to floor space. Electric Drive Electric robots are smaller and have better accuracy and repeatability.
They occupy less floor space and. 3 according to degrees of freedom. Two-coordinate robots three-coordinate robots four-coordinate robots five-coordinate robots six-coordinate robots.
Robotic systems are generally defined as Cartesian coordinate systems. Robot World Coordinate System. Robot origin coordinate system or ROBROOT coordinate system.
Workpiece and or BASE coordinate system. Robot Tool coordinate system. The ROBOOT-Koordinatensystem is a cartesian coordinate system which has its origin at the footprint of a robot.
It describes the position of the robot. Robots with a cylindrical coordinate system have a relatively simple structure where one twisting joint T is added to two typical linear coordinates L. Such type of robots are used for loading-unloading operations for packing palletizing etc.
In cases where the robots task is to move between different objects in the workplace. Robots are being classified on the basis of their physical configuration and control systems adopted. These classifications are briefly described as follows.
1Classification on the Basis of Physical Configurations On the basis of physical configuration industrial robots are classified in four different types. Robot Classification and Robot Reach Classification based on Physical configurations four basic configurations are identified with most of the commercially available industrial robots. Consist of links connected by linear joints L.
A is designated as LLL they are also called rectilinear robots. A first distinction can be done based on the mechanical structure of robots. They can be divided into fixed robots ie.
Manipulators Figure 2 and mobile robots. Furthermore mobile robots can be divided into wheeled tracked legged and undulating 3. A second and more meaningful classification is done according to the working environment.
