Boiling Point BP Carbon dioxide changes its state from liquid to gas at -78464C -1092352F or 194686K Carbon dioxide is a colorless odorless incombustible gas resulting from the oxidation of carbon. The view cell shown here has a glass tube inserted in the cell.
Boiling Point BP Carbon dioxide changes its state from liquid to gas at -78464C -1092352F or 194686K Carbon dioxide is a colorless odorless incombustible gas resulting from the oxidation of carbon.
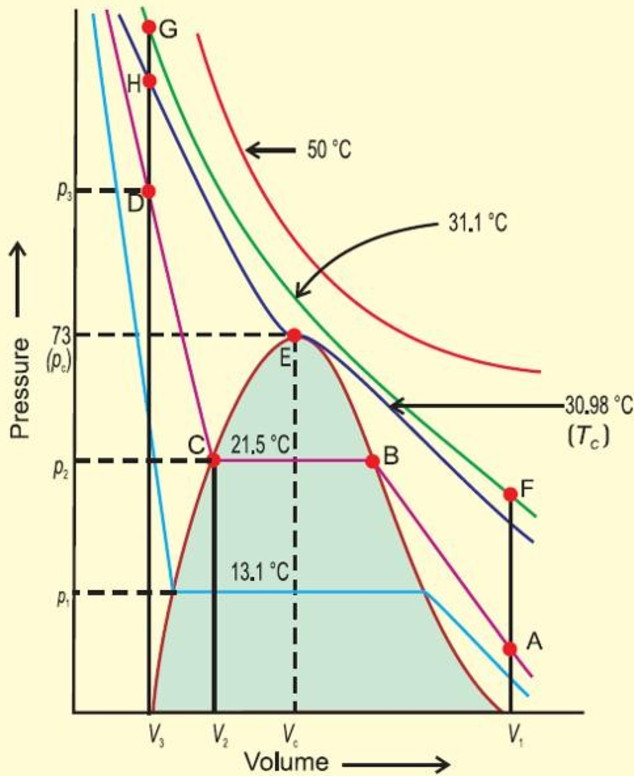
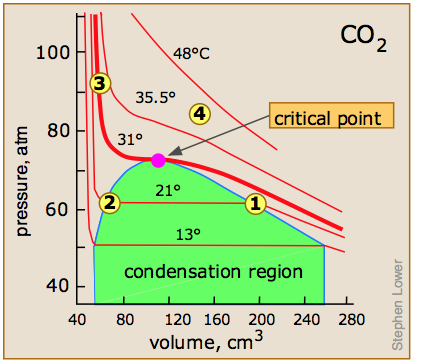
Critical volume of carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a gas at standard conditions. However at low temperature andor high pressures the gas becomes a liquid or a solid. The phase diagram for carbon dioxide shows the phase behavior with changes in temperature and pressure.
The curve between the critical point and the triple point shows the carbon dioxide boiling point with changes in pressure. The curve between the triple point downwards. Carbon dioxide is a popular supercritical fluid and has a critical temperature of 311 C and a critical pressure of 738 bar.
A high pressure stainless steel view cell apparatus with a quartz window is used to demonstrate the critical point of carbon dioxide. The view cell shown here has a glass tube inserted in the cell. The cell is filled with carbon dioxide and heated to the desired temperature.
Carbon dioxide CO2 CID 280 - structure chemical names physical and chemical properties classification patents literature biological activities safetyhazardstoxicity information. Tc 3041282 K 309782 C Critical temperature. Tc 8776076 F.
Thermodynamic Properties - Main. The atmosphere of Venus is composed mainly of carbon dioxide 965 and nitrogen 35. Because the atmospheric pressure at the surface of Venus is higher than 9 MPa and the mean temperature is over 700 K it is clear after consulting Table 1 that both of these substances exist as supercritical fluids.
Calculation of thermodynamic state variables of carbon dioxide at saturation state boiling curve. Lower limit for calculation. -55 C 54 bar bar upper limit.
30 C 7214 bar. BarMillibarMPak PaPascalN mm2kp cm2 atülb feet2psi lb inch2Torr mm Hginch Hgmm H2Oinch H2Ofeet H2O. Boiling Point BP Carbon dioxide changes its state from liquid to gas at -78464C -1092352F or 194686K Carbon dioxide is a colorless odorless incombustible gas resulting from the oxidation of carbon.
Carbon C Oxygen O Molecular weight. In this investigation I will aim to investigate the factors affecting the volume of carbon dioxide gas produced when Calcium carbonate reacts with Hydrochloric acid. This is shown in the equation below.
CaCo HCL CaCl Co H O. Calcium Carbonate Hydrochloric acid Calcium Chloride Carbon dioxide water. My results will be in cmï½.
I will workout my predicted results with the help of the. Critical temperature Critical pressure Boiling temperature 1 atm F C psi lbin 2 bar F C Air-22094-14052. 37858–Ammonia NH 3 270.
Carbon-dioxide CO 2 878. Solution for Carbon Dioxide has a critical temperature of 30413 K critical pressure of 73773 kPa and critical volume of 941 x 10 m mol By using the Van der. Rutgers University - Chem 171Week 11 - Molar Volume of Carbon DioxideWith Matt Stuber and Corey Frank.
The difference between the volumes of 0002 N sodium thiosulfate solution used in the two titrations should not be more than 05 ml. Pass a sample of liquid carbon dioxide from storage container or sample cylinder through a commercial carbon dioxide snow horn directly into an open clean container. Weigh 500 g of this sample into a clean beaker.
Allow the carbon dioxide. Critical parameters of mixtures of carbon dioxide and ethane articleAbbaci1992CriticalPO titleCritical parameters of mixtures of carbon dioxide and ethane authorA. Sengers journalInternational Journal of Thermophysics year1992 volume13 pages1043-1052.
The specific heat at constant volume of carbon dioxide in the neighbourhood of the critical point articleMichels1950TheSH titleThe specific heat at constant volume of carbon dioxide in the neighbourhood of the critical point authorA. Nonlinear Phenomena year1950 volume. Carbon dioxide arrives in the lung as dissolved carbon dioxide carbonic acid carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions for elimination by pulmonary gas exchange.
In a normal adult normal ventilation disposes of an average of 10000 to 15000 mmol of carbon dioxide per day. As the dissolved carbon dioxide diffuses across the alveolar membrane and plasma carbon dioxide levels decrease carbonic acid in the red blood cells is converted into carbon dioxide.