
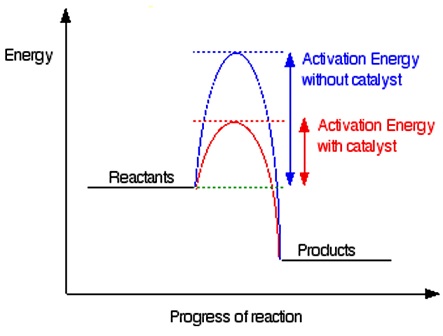
This speeds up that chemical reaction. Catalysts decrease the activation energy required for a reaction to proceed shown by the smaller magnitude of the activation energy on the energy diagram in.
Carbon and oxygen combine to form carbon dioxide and.
Do catalysts decrease activation energy. Catalyst decreases the activation energy of the reaction and helps to increase the reaction rate Examples of Chemical reactions require Activation energy The combustion reaction requires activation energy. Carbon and oxygen combine to form carbon dioxide and. Without being consumed in the reaction catalysts will lower the activation energy and boost the reaction rate.
Differences in the reactants inherent structures can lead to differences in reaction rates. Catalyst affects the activation energy by lowering the reaction pathway. Catalyst lower the activation energy requires by the particles of reactants to give a product this result in formation of a product in a time less than the time taken for the reaction in the absence of a catalyst.
Catalysts increase the rate with which a biochemical reaction takes place by lowering the activation energy required for that reaction to proceed. See full answer below. Catalysts are substances that lower the activation energy and thereby increase the rate of reactions.
Catalysts are essential in the production of industrial chemicals. Adding a catalyst has exactly this effect of shifting the activation energy. A catalyst provides an alternative route for the reaction.
That alternative route has a lower activation energy. Showing this on an energy profile. A catalyst provides an alternative route for the reaction with a lower activation energy.
It does not lower the activation energy of the reaction. There is a subtle difference between the two statements that is easily illustrated with a simple analogy. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
The point missing so far in the answers is that a catalyst causes the reaction to occur by a different mechanism than it would normally take. This is why its actually very hard to find good catalysts The catalyst lowers the activation energy but its not the same barrier as without the catalyst. So in that sense it does not lower the barrier as commonly stated.
As a result the rate of reaction increases. To illustrate how a catalyst can decrease the activation energy for a reaction by providing another pathway for the reaction lets look at the mechanism for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by the I - ion. However if a catalyst is added to the reaction the activation energy is lowered because a lower-energy transition state is formed as shown in Figure 3.
Enzymes can be thought of as biological catalysts that lower activation energy. Enzymes are biological catalysts for lowering activation energy - the speed up the rate of reactions and all allow biological reactions involved in metabolic processes to take place at body temperature 37C. They lower the energy of that transition state and so they decrease the activation energy.
This speeds up that chemical reaction. This speeds up that chemical reaction. When they act on chemical reactions enzymes do not change the Gibbs free energy which means they do not increase or decrease how much products are formed at the end of that reaction.
Catalysts work by lowering the activation energy a reaction needs in order to proceed. It lowers the hill. It does this by creating a different pathway for the reaction to take to get to its final.
Catalysts decrease the activation energy required for a reaction to proceed shown by the smaller magnitude of the activation energy on the energy diagram in. Acid Base catalysis Chemical groups are made more reactive by adding or removing a proton from substrate to reduce stabilizing transition state free energy. - Result of AcidBase catalysis is making a reactive group more reactive by increasing its intrinsic electrophilic or nucleophilic character - This can increase the rate 10-100 fold.
Catalysts are substances that increase the reaction rate by lowering the activation energy needed for the reaction to occur. Enzymes act as a catalyst by lowering the activation energy required to initiate the biochemical reaction.