
These acute cardiac adaptations caused by acute PE event were summed up as RVD. The RV systolic pressure was statistically different between types except for types C and D.
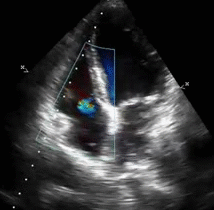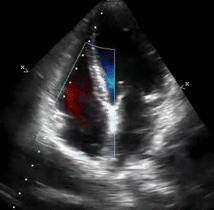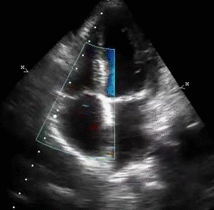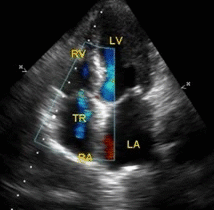
Of the 22628 patients who had undergone echocardiography 10905 had RVSP measured.
Elevated right ventricular systolic pressure. The right ventricular pressure is most commonly elevated because of an unobstructed ventricular component of the atrioventricular septal defect. Right ventricular hypertension however can also reflect increased left atrial pressure and pulmonary hypertension. This can be produced for example by an associated partition within the left atrium or by left-sided malalignment of the atrial relative to the.
The right ventricular systolic pressure RVSP may be used in the evaluation of pulmonary valve stenosis. It is based on measuring the TR jet maximum velocity by continuous wave CW spectral Doppler. If there is no significant stenosis then the RVSP may be equivalent to the systolic pulmonary artery pressure SPAP.
RVSP 4 x TR V max 2 RAP. Elevated right ventricle pressure resulting from pulmonary artery stenoses may affect outcome and survival after liver transplantation in patients with Alagille syndrome. An abrupt increase of afterload seen in cases of acute PE event lead to elevated right ventricular wall tension that could result in right ventricular dilatation hypokinesis and secondary tricuspid regurgitation.
These acute cardiac adaptations caused by acute PE event were summed up as RVD. In acute PE presence of RVD or myocardial necrosis is associated with increased mortality. RVSP was calculated from the peak tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity V using the modified Bernoulli equation RVSP 4V2 RAP with the mean right atrial pressure RAP estimated to be 10 mmHg.
Of the 22628 patients who had undergone echocardiography 10905 had RVSP measured. All abnormal echocardiograms were excluded leaving 1559 echocardiograms for analysis. Acutely the right ventricle is unable to generate a systolic pressure greater than 50 mm Hg.
A higher systolic value suggests a chronic process with right ventricular hypertrophy. An estimated right ventricular systolic pressure eRVSP a measure of the pressure inside the artery that supplies blood to the lungs pulmonary artery greater than 300 mmHg is related to an increased risk of mortality in patients with pulmonary hypertension PH according to a new Australian study. When dividing by gestational age categories the association between systolic blood pressure and LV mass index in the adjusted regression models was significant across all groups but was greatest in those born very and extremely preterm systolic blood pressure compared.
If there is enough to make me worry about PAH then I generally move forward and perform a right heart catheterization. Patients with advanced lung disease often have mildly elevated pulmonary artery pressures and this is a different disease than PAH. Patients with left heart problems also often have minimally elevated pulmonary artery pressures and this is also not PAH.
Systemic hypertension occurs when blood pressure is abnormally high in the aorta and its branches left sided circulation. This pressure is obtained with a blood pressure machine and a cuff. Pulmonary hypertension occurs when there is abnormally high blood pressure in the pulmonary artery and its branches right sided circulation.
In common with other types of pulmonary hypertension these changes result in an increased workload for the right side of the heart. The right ventricle is normally part of a low pressure system with systolic ventricular pressures that are lower than those that the left ventricle normally encounters. Adding the transtricuspid gradient to the mean right atrial pressure estimated clinically from the jugular veins gave predictions of right ventricular systolic pressure that correlated well with catheterization values r 93 SEE 8 mm Hg.
The tricuspid gradient method provides an accurate and widely applicable method for noninvasive estimation of elevated right ventricular systolic pressures. Right ventricular wall stress summarizes the major factors that contribute to wall stress on the right ventricle including pressure dilation or radius and wall thickness. Note that the right ventricular wall stress is low in normally functioning ventricles and the right ventricular wall stress is high in those with severe systolic dysfunction.
38 Right ventricular pressure. 38 Pulmonary artery pressure. 412 Pulmonary vein Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure.
215 Left ventricular pressure. The RV systolic pressure ranged from 18 to 55 mm Hg mean 34 - 1 in type A 46 to 55 mm Hg 50 - 1 in type B 60 to 76 mm Hg 66 - 2 in type C and 72 to 118 mm Hg 93 - 7 in type D. The RV systolic pressure was statistically different between types except for types C and D.
These data indicate that the end-systolic configuration of the VS in the short-axis 2-D echocardiogram may be useful for the semiquantitative assessment of the RV systolic pressure. Right ventricular systolic pressure hence pulmonary ar- terial pressure in the absence of right ventricular outflow tract obstruction has been accurately predicted by con- tinuous wave Doppler ultrasound using the tricuspid sys- tolic gradient methods6 However this method may not be very useful in patients with ventricular septal defect in whom tricuspid regurgitation is uncommon. Chronically hypertrophied right ventricles function normally under high systolic pressures whereas normal right ventricles fail when they are acutely subjected to similar pressures.
This phenomenon may be partly due to adaptation of the coronary circulation as well as to hypertrophy. Knowledge of the magnitude and distribution of coronary blood flow and the degree of coronary vascular reserve.