A system that is open will contain or interact with parts of the local environment while a closed system does not interact with the local environment at all. For example cattle ranching and extensive grain cultivation in the USA Canada and Australia.

A similar systems-based planning.
Examples of farming systems. A system that is open will contain or interact with parts of the local environment while a closed system does not interact with the local environment at all. For example a greenhouse lettuce farm is a relatively closed environment compared to an outdoor lettuce farm. 25 Mixed Farming Dairy Beef Cattle or Swine and Cropping Systems.
In mixed farming systems cropping systems usually revolve around forage or feed requirements of the livestock which contribute manure for crop production. Because of manure and also because a part of the crop acreage is under soil-protective perennial forage cropping mixed farming is considered to be more sustainable than. Your presentation should be accompanied by a hand out for everybody to use to revise from.
Tropical commercial Plantation agriculture in MalaysiaExtensive commercial pastoralism in the Pampas Irrigation agriculture in the Nile ValleyIntensive subsistence farming in the Ganges ValleyIntensive commercial mixed agriculture in the NetherlandsFor each you will need not more than 3 slides on where it is how the farming functions as a system. Shifting cultivation is an example of farming in which labour and capital are both low but large areas are covered. 2 Labour is limited and capital higher.
For example cattle ranching and extensive grain cultivation in the USA Canada and Australia. Types of Integrated Farming System Crop-Livestock Farming System Crop-Livestock-Fishery Farming System Crop-Poultry-Fishery-Mushroom Farming System Crop-Fishery-Duckery Farming System Crop-Livestock-Fishery-Vermicomposting Farming System Crop-Livestock-Forestry Farming System Agri-Silvi-Apiary Farming System Agri-Horti-Silvi-Pastoral Farming System. Mixed farming bushing fallowing shifting cultivation and pastoral farming are the three major types of farming system.
Normadic farming Ley farming and Ranching are the three types of Pastoral farming. Factors that determines the Adoption of a farming systems are The social factors environmental factors and Land tenure. Agricultural and particularly farming systems exhibit great diversity as shown by eg Duckham and Masefield 1970 Grigg 1974 Kostrowicki 1974 and Ruthenberg 1980.
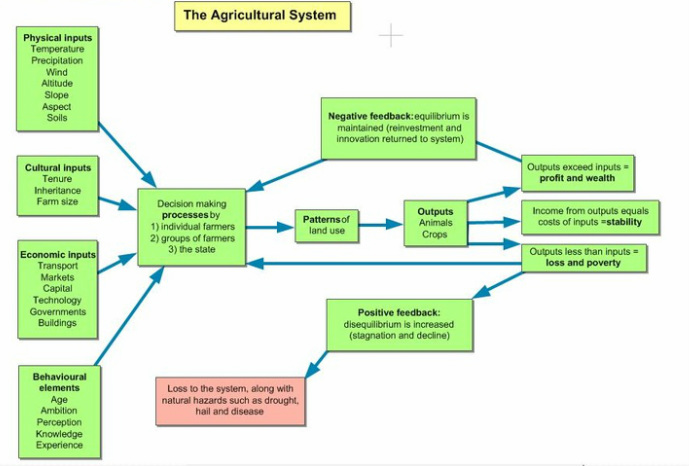
They have been classified in various ways as reviewed by Fresco and Westphal 1988 who also present an ecologically-based classification and typology of farm systems. The Agriculture System W. Caldwell 2 treatment of natural heritage areas.
Provincial policy requires the proactive identification of natural heritage systems so that the most important areas can be protected and their ecological functions maintained for example. A similar systems-based planning. Agricultural Systems is an international journal that deals with interactions - among the components of agricultural systems among hierarchical levels of agricultural systems between agricultural and other land use systems and between agricultural systems and their natural social and economic environmentsManuscripts submitted to Agricultural Systems generally should include both of the.
A range of farming practices has been emerged to increase the productivity of the agricultural land. Two such farming practices are intensive farming and extensive farming. Intensive Farming is a farming method that uses higher inputs and advanced agricultural techniques to.
Desmodium eliminates Striga weeds and repels the stemborers which are instead attracted to the elephant grass. By growing Desmodium the familys farm has become a source of seeds for scaling up the push-pull technology in the whole region.