
Inside your cells the individual amino acids can bond together by forming a peptide bond which is simply a chemical bond that joins amino acids together. Polypeptide chains are formed when several peptide chains interact.
It is abbreviated as tRNA where the t stands for transfer.
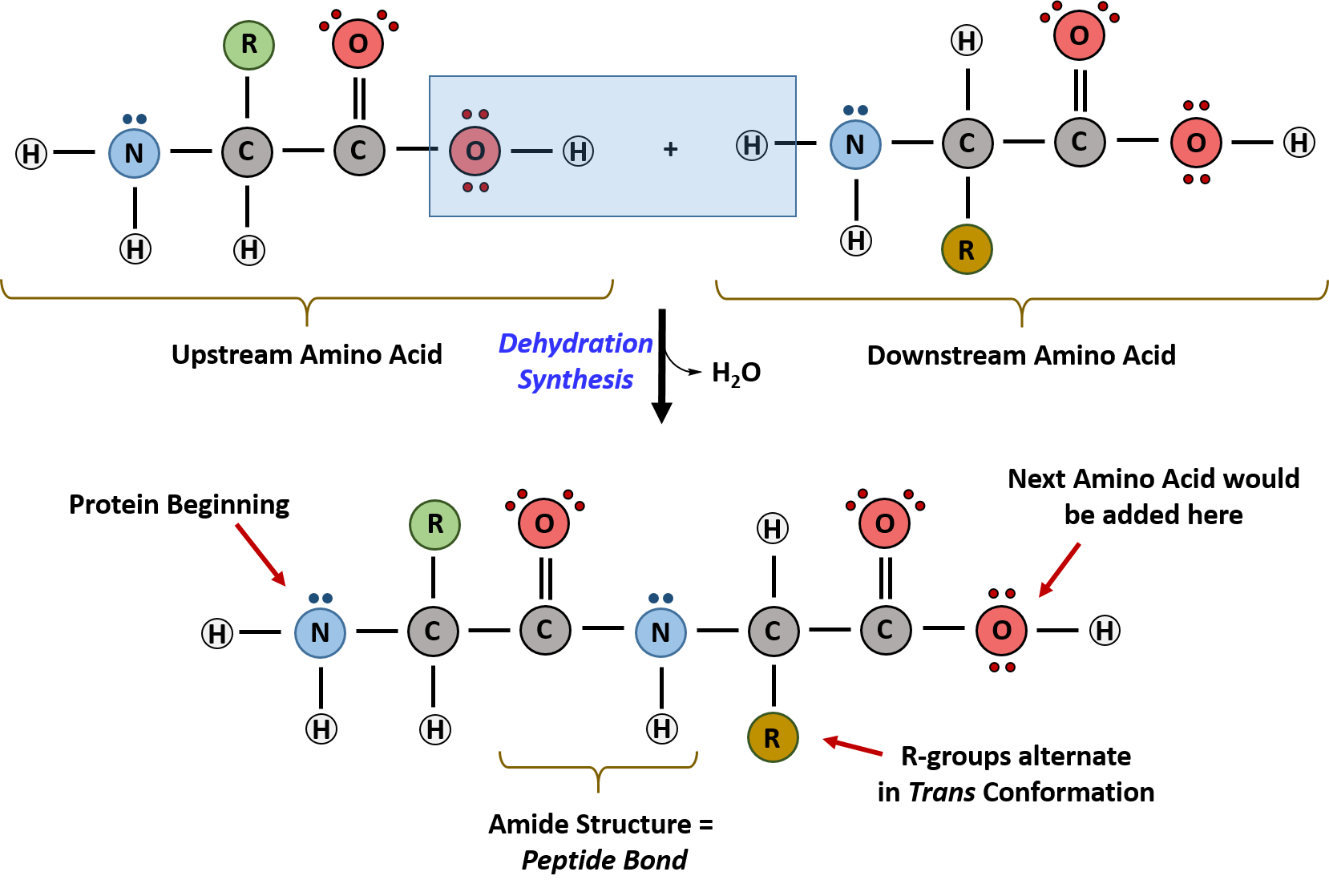
Formed from amino acids. Amino acids condense to produce peptides. Generally condensation reaction occurs between a primer amino acid or peptide and another amino acid. Molecule of water is eliminated.
The bond thus formed NHCO is actually amide bond which is popularly known as peptide bond or linkage. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Specifically a protein is made up of one or more linear chains of amino acids each of which is called a polypeptide.
Well see where this name comes from a little further down the page There are types of amino acids commonly found in proteins. Amino acid any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group NH 2 an acidic carboxyl group COOH and an organic R group or side chain that is unique to each amino acid. The term amino acid is short for α-amino alpha-amino carboxylic acid.
Each molecule contains a central carbon C atom called the α-carbon to which both an amino and a carboxyl group are attached. Inside your cells the individual amino acids can bond together by forming a peptide bond which is simply a chemical bond that joins amino acids together. More specifically peptide bond.
Amino acids are organic molecules that when linked together with other amino acids form a protein. Amino acids are essential to life because the proteins they form are involved in virtually all cell functions. Some proteins function as enzymes some as antibodies while others provide structural support.
Although there are hundreds of amino acids found in nature proteins are constructed from a. In an α helix the carbonyl CO of one amino acid is hydrogen bonded to the amino H N-H of an amino acid that is four down the chain. Eg the carbonyl of amino acid 1 would form a hydrogen bond to the N-H of amino acid 5.
Amino acids are organic compounds that come together to form proteins in your body. There are 20 amino acids overall and they each fall into one of three categories. A polymer formed of amino acids is a polypeptide named from the numerous peptide bonds in the chain.
One peptide bond links two amino acids. Two amino acids joined form a. As mentioned above a peptide bond is the main reaction between amino acids in the formation of proteins.
However protein formation is a multi-step process. Individual amino acids join with other amino acids through peptide bonds to form peptide chains. Polypeptide chains are formed when several peptide chains interact.
Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form protein. Peptide bonds are formed by the biochemical reaction that extracts a water molecule when the two amino acids are joined together. Interesting Facts about Proteins and Amino Acids.
We get amino acids from basic foods such as chicken bread milk nuts fish and eggs. Hair is made up of a protein called keratin. A special kind of RNA called transfer RNA moves the amino acids to the ribosome.
It is abbreviated as tRNA where the t stands for transfer. Amino acids can be classified as being glucogenic or ketogenic based on the type of intermediates that are formed during their breakdown or catabolism. The catabolism of glucogenic amino acids produces either pyruvate or one of the intermediates in the Krebs Cycle.
The catabolism of ketogenic amino acids produces acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl COA see Figure 1. In a normal diet containing 60 - 100 grams of protein most of the amino acids are used for the synthesis of proteins in the liver and in other tissues. Carbon skeletons of excess amino acids may be oxidized for energy converted to fatty acids or in some physiological situations converted to glucose.
Anybody who frequently visits the gym knows that amino acids are the building blocks of protein but they also fulfill the foundation for well-being. 1 In pure form amino acids are white crystalline solids with limited solubility in water. 2 In an alpha-helix structure all of the amino acid side chains lie outside the helix.
3 Protein denaturation affects all four levels of protein structure. First evidence that amino acids formed soon after the Big Bang A new measurement of chemical evolution suggests that amino acids filled the early universe some nine billion years before life.