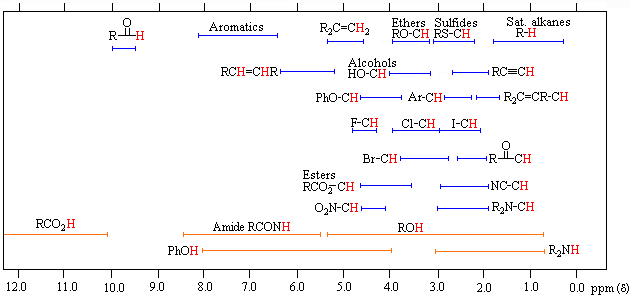
Be aware that the exact substitution pattern around a particular H causes changes in the chemical shift and therefore ranges of values are given in the tables and the above figure. Table of characteristic proton NMR chemical shifts.

After preparing the solutions and a second time 24 h after preparation to assess the stability of the CoA species.
H nmr spectrum table. Overview of typical 1H NMR shifts 1H NMR Tables. FROM TABLE 144 LABBOOK OR TABLE H6 SPEC BOOK FROM TABLE 146 LABBOOK OR TABLE H4 SPEC BOOK 58 50 52 61. CALCULATING THE IH NMR CHEMICAL SHIFTS OF ALKENES able 144 Calculation ofÄH NMR Chemical Shifts for Alkenes See Figure 1412 for more information.
As 097 093 -106. 1H NMR Tables Overview of typical 1H NMR shifts Note. Alkene region modified from earlier handout.
Table 132 Regions of the IH NMR Spectrum Halogen Chemical shift ô c I Allylic c Saturated I Aromatic cc Vinylic Table 133 Correlation of IH Chemical Shift with Environment c c c c 0 c 0 H H Chemical shift 6 25-50 3345 4565 65-80 97-100 110-120 Type of hydrogen Reference Alkyl primary Alkyl. 1H NMR Chemical Shifts 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 RH O H R 2CCR H ROCH 3 CH 3 RCH 3 O RH CH 3 CH NH OH RNH 2 O NH 2 RNH 2 ROH O OH ROH δ ppm Type of C-Hδ ppmDescription of Proton 09 alkyl methyl 13 alkyl methy lene 15-2alkyl methine 18 allylic C is next to a pi bond 2-23α to carbonyl C is next to CO 23 benzylic C is next. In the nmr spectrum of the dianion the innermost methylene protons red give an nmr signal at 222 ppm the adjacent methylene protons blue give a signal at 126 ppm and the methyl protons green a signal at 56 ppm.
Lets start with the chemical shift of protons of alkyl C-H groups. The Chemical Shift of Connected to sp 3 Hybridized Carbons. We can see in the table that sp3 hybridized C H bonds in alkanes and cycloalkanes give signal in the upfield region shielded low resonance frequency at the range of 12 ppm.
The only peak that comes before saturated C-H protons is the signal of the protons. 1H 1D NMR Spectrum Peak Chemical Shift ppm A 0 B 296 C 514 D 770 E 110 F 111 G 114 H 132 I 135 J 152 K 169 13C 1D NMR Spectrum The DMA concentrationin the samplewas 100mM. All data were.
The table below summarizesthe data of each chemicalshift to the. After preparing the solutions and a second time 24 h after preparation to assess the stability of the CoA species. For a few representative tissue extracts 1D NMR spectra were also obtained before and after spiking with solutions of the authentic compounds to confirm the identified peaks Table S1.
To measure T 1 relaxation times for the. To each tube 50 µL of the stock solution and 3 µL of TMS1 were added. The solvent chemical shifts3 were obtained from the spectra containing the solutes and the ranges of chemical shifts 1 For recommendations on the publication of NMR data see.
IUPAC Commission on Molecular Structure and Spectroscopy. Apiezon H grease hexamethylbenzene hexamethyldisil-oxane imidazole pyrrole and pyrrolidine have also beenaddedtothisexpandedlist. Experimental Section All deuterated solvents were obtained commercially through Cambridge Isotope Laboratories Inc.
NMR spectra were recorded at 298 K using 300 500 or 600 MHz spectrometers. 1H-NMR Chemical Shift Table 105 90 80 65 130 100 78 65 80 50 88 76 14 135 13 125 12 115 11 105 10 95 9 85 8 75 7 65 6 ppm H H O OH O H HO N H O N H. Chemical Shift Tablexls Author.
Matt Bowman Created Date. 1 H NMR Chemical Shifts. Chemical shift is associated with the Larmor frequency of a nuclear spin to its chemical environment.
TetramethylsilanTMSCH 3 4 Si is generally used for standard to determine chemical shift of compounds. In other words frequencies for chemicals are measured for a 1 H or 13 C nucleus of a sample from the 1 H or 13 C resonance of TMS. Once a NMR spectrograph is recorded 4 pieces of information can be determined from the data as long as the chemical formula of the compound is known.
To illustrate the points we will consider the following 1 H-NMR spectrum of the C 5 H 10 O. Signal Count Number of unique hydrogens. This is the easiest to interpret.
SPECTROSCOPIC TABLES The following pages contain some basic spectroscopic data tables. 1 Schematic diagrams of NMR chemical shift data for H Both the schematic figure and the table show similar information presented in different ways. Both have their merits.
They show the typical chemical shifts for protons being influenced by a single group. Be aware that the exact substitution pattern around a particular H causes changes in the chemical shift and therefore ranges of values are given in the tables and the above figure. Having a good feel for the typical chemical shifts will save yourself lots of time in examinations and avoid confusion.
An example of an H NMR is shown below. Table of characteristic proton NMR chemical shifts. Type of proton type of compound chemical shift range ppm RC H 3 1 aliphatic 09 R 2 C H 2 2 aliphatic 13.
There are generally three possible ways for aromatic peaks to appear in a H NMR spectrum when only one group is attached the ring. STRONG DEACTIVATING GROUPS have a partially positive atom attached directly to ring. These include CO NO2 CN and SO groups.
This often produces a split into two peaks centered at. In Figure PageIndex3 an 1 H NMR spectra of ethanol we can see a clear example of chemical shift. There are three sets of peaks that represent the six hydrogens of ethanol C 2 H 6 O.
The presence of three sets of peaks means that there are three different chemical environments that the hydrogens can be found in. The terminal methyl CH 3 carbons three hydrogens the two hydrogens.