Inertial sen- sors based on microelectromechanical system MEMS technology have recently become commercially available at. Static positioning involves placing the receiver at a fixed location on the Earth and determining the position of that point.

1 The conventional approach to aiding the receivers carrier and code tracking loops with inertial sensor information allows the effective bandwidth of these loops to be reduced even in the presence of.
Ins gps integration for geodetic applications. The applications of GPS range from military navigation vehicle monitoring to sporting activities. For geodetic applications the precise measurement of baselines relative positioning in static mode of GPS is widely used. Static positioning involves placing the receiver at a fixed location on the Earth and determining the position of that point.
The integration of GPS and INS has been extensively investigated and increasingly applied for high precision position and attitude determination in different kinds of applications such as airborne geo-referencing and land vehicle navigation. With the availability of the Global Positioning System GPS and the decreasing costs of inertial navigation systems INS the direct measurement of the position and attitude parameters of. This book covers all aspects of inertial navigation systems INS including the sensor technology and the estimation of instrument errors as well as their integration with the Global Positioning.
This book covers all aspects of inertial navigation systems INS including the sensor technology and the estimation of instrument errors as well as their integration with the Global Positioning System GPS for geodetic applications. Complete mathematical derivations are given. INS and GPS integration Casper Ebbesen Schultz Kgs.
Lyngby 2006 IMM-MSc-2006-60. Technical University of Denmark Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Building 321 DK-2800 Lyngby Denmark Phone 45 45253351 Fax 45 45882673 receptionimmdtudk wwwimmdtudk. The goal of INSGPS integration besides providing the redundancy of two systems is to take advantage of the synergy outlined as follows.
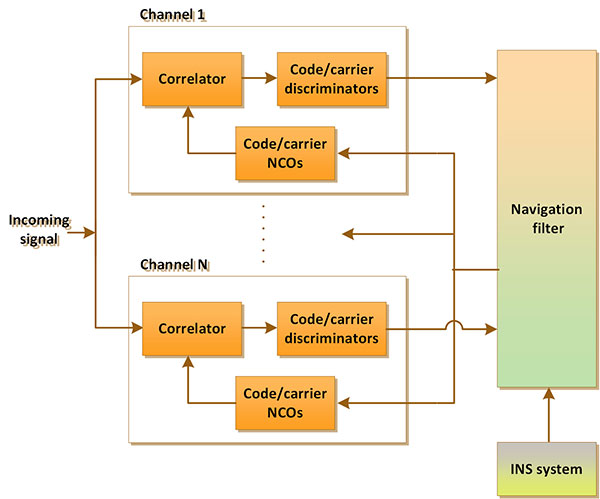
1 The conventional approach to aiding the receivers carrier and code tracking loops with inertial sensor information allows the effective bandwidth of these loops to be reduced even in the presence of. The integration of GNSSINS is very common for applications in which the GPS alone is not sufficient. In difficult environment like urban canyons generally high-end INS can be used but the great challenge is using low-cost inertial sensors characterized by their low weight and size and with poorer performance.
The integration of both systems INS and GPS can generate a navigation system capable of exploiting the advantages of both and also limits the drawbacks of the systems viewed by separate. Thus a GPS-aided INS can produce estimates of the full state of the vehicle both at high frequency as drift-free. The most common GNSSINS integration scheme is the so-called loosely-coupled where the positions and velocities derived by GNSS signal processing are merged as updates of the INS estimates positional information through a navigation Kalman filter 7.
Vector gravimetry using Inertial Navigation System INS in semi-kinematic mode has been successfully applied. The integration of INS with other sensors Global Positioning System GPS or Gradiometer for instance has been under investigation for many years. This dissertation examines the effect of photogrammetric derived orientation.
This book covers all aspects of inertial navigation systems INS including the sensor technology and the estimation of instrument errors as well as their integration with the Global Positioning. The Global Positioning System GPS has become a widely used tool in geodetic studies of Earth. We review the principles of the applications of GPS to geodetic problems and discuss its applications to problems of global and regional geodesy.
A global network of dual-frequency GPS receivers continuously tracks the GPS satellites and the data are distributed to globally accessible on. AbstractThe relatively high cost of inertial navigation systems INSs has been preventing their integration with global posi- tioning systems GPSs for land-vehicle applications. Inertial sen- sors based on microelectromechanical system MEMS technology have recently become commercially available at.
Master Clock SAASM GPS Aided INS Combined in a Single Enclosure. The Geo-PNT SAASM is an innovative and efficient solution for applications that need precise navigation data as well as accurate time reference. The Geo-PNT SAASM combines a high performance versatile GPS master clock with an accurate inertial navigation system that delivers position navigation and timing PNT under all.
The method is based on developing the error dynamics equations of the INS in the inertial frame where the INS system errors are estimated in a wave estimator using inertial GPS position as update. Then using the error-corrected INS acceleration and the GPS acceleration in the inertial frame the gravity disturbance vector is extracted. The integration of an Inertial Navigation System INS and the Global Positioning System GPS is common in mobile mapping and navigation applications to seamlessly determine the position velocity and orientation of the mobile platform.
Landau 1989 On the Use of GPS in Airborne Photogrammetry Hydrographic Applications and Kinematic SurveyingProc. 5th International Geodetic Symposium on Satellite Positioning Las Cruces March 1317 1989 10291040 Google Scholar. Applications V-STARS is routinely employed in high-accuracy 3D measurement tasks across a broad range of applications and industries.
Any sized object can be dimensionally recorded with V-STARS photogrammetric technology.