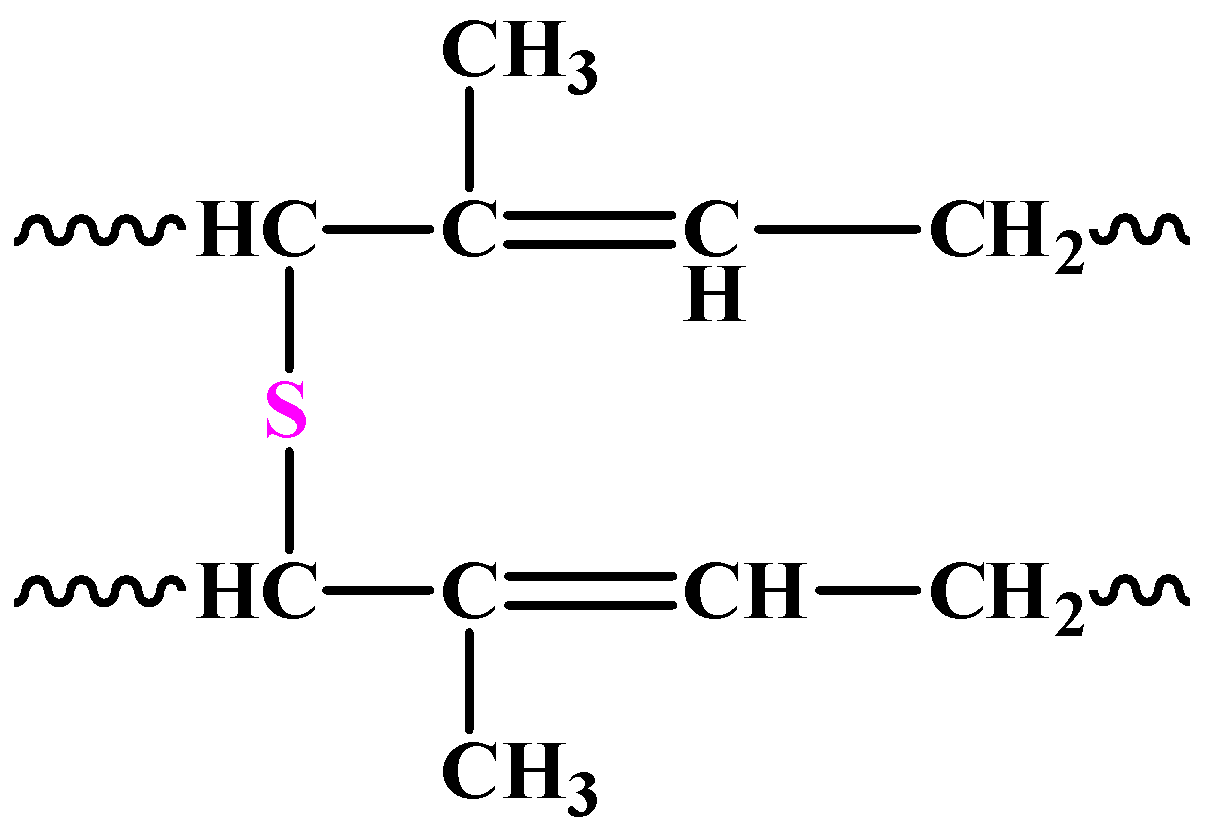
Part of ethylene-propylene rubber EPM and EPDM. When two hydrogen atoms are replaced the product name is based on the relative position of the replacement atoms or.
It is disclosed a toughened polyamide comprising a polyamide such as Nylon 6 and a minor amount of a linear alternating polymer of carbon monoxide and at least one or more ethylenically.
Natural rubber is a polymer of the following unsaturated hydrocarbon. Natural rubber is yet another useful polymer which is obtained from the latex of the rubber tree. The monomer units are of the unsaturated hydrocarbon 2-methyl-i 3-butadiene also called isoprene. Examples of natural polymers.
Natural rubber cellulose nucleic acids proteins etc. Natural rubber is a polymer a long chain like molecule that contains repeating subunits. The term polymer comes from the Greek poly meaning many and mer meaning parts.
The chemical name for natural rubber is polyisoprene. The monomer meaning one-part from which it is built is isoprene. It is worth mentioning here that although natural rubber is built of repeating isoprene units isoprene.
Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers. Currently rubber is harvested mainly in the form of the latex from the. Difference Between Natural Rubber and Synthetic Rubber Definition.
Natural rubber is a natural biosynthetic polymer obtained from a tree called Hevea brasiliensis. Synthetic rubber is man-made polymers under controlled conditions. Natural rubber as the name suggests naturally occurs in the plant cells.
Rubber Polymers Rubber is an example of an elastomer type polymer where the polymer has the ability to return to its original shape after being stretched or deformed. The rubber polymer is coiled when in the resting state. The elastic properties arise from the its ability to stretch the chains apart but when the tension is released the chains snap back to the original position.
The majority of rubber polymer. The following article is from The Great Soviet Encyclopedia 1979. It might be outdated or ideologically biased.
Rubber Natural caoutchouc crude rubber a polymer of plant origin the vulcanization of which produces processed rubber. Natural rubber is one of the elastomers a group of macromolecular compounds that possess the capacity for. Part of the monomer is lost when forming polymer.
Chain of carbon atoms. The chains or groups coming off the backbone. A process in which rubber is reacted with sulfur to Harden the rubber.
Polymers that are not carbon based molecules. Cheremisinoff PhD in Condensed Encyclopedia of Polymer Engineering Terms 2001 AROMATIC. Unsaturated hydrocarbon identified by one or more benzene rings or by chemical behavior similar to benzene.
The benzene ring is characterized by three double bonds alternating with single bonds between carbon atoms compared with olefins. A polymers which has found significant commercial applications in fibers. Wood rubber cotton wool leather and silk are examples of.
Naturally occurring polymers derived from plants and animals. A hydrocarbon containing one or more benzene rings or other similarly stable electron arrangements is an aromatic hydrocarbon and any related substance is an aromatic compound. One or more of the hydrogen atoms on a benzene ring can be replaced by other atoms.
When two hydrogen atoms are replaced the product name is based on the relative position of the replacement atoms or. Natural rubber latex is produced by over 2000 plant species and its main constituent is polycis-14-isoprene a highly unsaturated hydrocarbonSince 1914 there have been efforts to investigate microbial rubber degradation. However only recently have the first proteins involved in this process been identified and characterized and have the corresponding genes been cloned.
Polymers have been essential components of commodities since the early days of humankind. The use of wool cotton and linen fibres for garments paper reed for paper are just a few examples of how our ancestors exploited polymer-containing raw materials to obtain artefacts. The latex sap of cautchouc trees natural rubber reached Europe in the 16th century from South America long.
Natural rubber for example is a hydrocarbon that contains long chains of alternating CC double bonds and C C single bonds. Writing the structure of complex hydrocarbons can be simplified by using a line notation in which a carbon atom is assumed to be present wherever a pair of lines intersect and enough hydrogen atoms are present to satisfy the tendency of carbon to form a total of four bonds. Natural rubber see above Natural occurrence is a polymer of 2-methyl-13-butadiene commonly called isoprene.
Coordination polymerization conditions have been developed that convert isoprene to a polymer with properties identical to that of natural rubber. It is disclosed a toughened polyamide comprising a polyamide such as Nylon 6 and a minor amount of a linear alternating polymer of carbon monoxide and at least one or more ethylenically. Derived from the Greek word poly meaning many and meros meaning part.
A polymer consists of a long molecular chain made of equal units monomers. Chemical reaction where several molecules of the same type are united to produce a bigger unit. Unsaturated hydrocarbon CH 2 CHCH 3.
Part of ethylene-propylene rubber EPM and EPDM. A composition comprising a polymer of an unsaturated hydrocarbon a C 1-4 alkyl or hydroxyalkylether of starch having a degree of substitution of at least 025 and a polyhydric aliphatic alcohol having 2 to 10 carbon atoms and 2 to 6 hydroxyl groups wherein the compatibilizing agent can be a vinyl copolymer acrylic polymer and mixtures thereof. Technically speaking natural rubber is an elastomer or an elastic hydrocarbon polymer.
Natural rubber NR is a critical and strategic industrial raw material for manufacturing a wide variety of products ranging from medical devices and personal protective equipment to aircraft tires Hobhouse 2005. Car tires are made of 1214 different rubbers with up to 50 NR content. Aircraft and race tires contain only NR.
