In the first step of DNA replication unzip the double helix of DNA molecule. Was developed by the British biochemist Fred Sanger and his colleagues in 1977.

Starting DNA Replication.
Organize the sequence of events in dna replication. Describe the sequence of events that occur during DNA replication. DNA replication begins with the unzipping of the double stranded DNA by the enzyme DNA helicase which breaks hydrogen bonds as it separates the strands. Another enzyme known as topoisomerase holds the two DNA strands apart whilst helicase works.
Once the two strands are separate. The process of DNA replication is a complex one and involves a set of proteins and enzymes that collectively assemble nucleotides in the predetermined sequence. In response to the molecular cues received during cell division these molecules initiate DNA replication and synthesize two new strands using the existing strands as templates.
Each of the two resultant identical DNA molecules is. When the aya1 gene is mutated Schizosaccharomyces pombe cells become unable to react appropriately to a delay in DNA replication. Instead of stalling the cell cycle to allow completion of DNA synthesis they proceed unperturbed towards mitosis and attempt to segregate the still unreplicated chromosomes.
As a result the genetic material segregates unevenly and the nuclei assume a mitotic. DNA replication is the production of identical DNA helices from a single double-stranded DNA molecule. Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand.
Prior to replication the DNA uncoils and strands separate. A replication fork is formed which serves as a template for replication. Primers bind to the DNA and DNA polymerases add new nucleotide sequences.
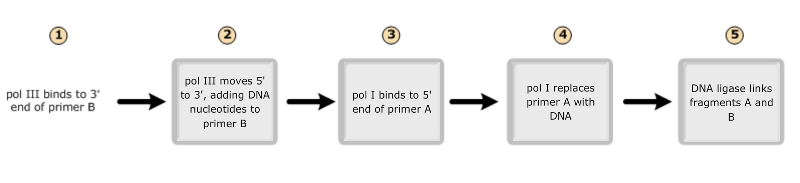
The mechanism of DNA replication. DNA replication takes place in three major steps. Opening of the double-stranded helical structure of DNA and separation of the strands.
Priming of the template strands. Assembly of the newly formed DNA segments. During the separation of DNA the two strands uncoil at a specific site known as the origin.
With the involvement of several enzymes and proteins they prepare prime the strands. Find an answer to your question ill mark brainliest explain the sequence of events in the replication of DNA kittyneck kittyneck 02212021 Biology High School answered Ill mark brainliest explain the sequence of events in the replication of DNA 1 See answer kittyneck is waiting for your help. Add your answer and earn points.
Starting DNA Replication. In the process of DNA replication DNA made a copy of itself during the cell division. In the first step of DNA replication unzip the double helix of DNA molecule.
Secondly the enzyme named as helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds by holding the complementary bases of DNA together. In last one of the strands is oriented in the 3 to 5 direction. DNA replication occurs by three steps.
DNA replication in prokaryotes. DNA replication begins from origin. In E coli replication origin is called OriC which consists of 245 base pair and contains DNA sequences that are highly conserved among bacterial replication.
Find an answer to your question what are the sequence of events in the replication of DNA. Start studying summary of events at the DNA replication fork. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
DNA replication starts at a specific sequence the origin on the chromosome and proceeds in two directions towards another specific region the terminusNumber of Upcoming conferencesWorkshopsSymposiums are 5 in numberAround 5 companies are there which actively involved in the process of replication and its research. It includes the events occurring at the replication fork where the parent poly-nucleotides are copied. It is less understood.
It occurs when the parent molecule has been completely replicated. In a cell DNA replication begins at specific locations in the genome called origins. In case of E.
Coli the origin of replication is a sequence of approximately 245 base pairs bp called oriC. Origins contain DNA sequences recognized by replication. Energy of Replication The nucleotides arrive as nucleosides DNA bases with PPP P-P-P energy for bonding DNA bases arrive with their own energy source for bonding bonded by enzyme.
DNA polymerase III ATP GTP TTP CTP. When DNA replicates each new DNA molecule contains half of the original molecule. When cells reproduce the new cell needs a copy of the DNA.
The two DNA strands do not go in the same direction. The process of DNA replication is catalyzed by a type of enzyme called DNA polymerase poly meaning many mer meaning pieces and ase meaning enzyme. So an enzyme that attaches many pieces of DNA.
During replication the two DNA strands separate at multiple points along the length of the chromosome. These locations are called origins of replication because replication begins at these points. The double helix of the original DNA.
Explore the steps of DNA replication the enzymes involved and the difference between the leading and lagging strand. This video is an update from our old D. Is the process of determining the sequence of nucleotide bases As Ts Cs and Gs in a piece of DNA.
Was developed by the British biochemist Fred Sanger and his colleagues in 1977. It was the first practical method for determining the order for the nucleotides of a sample of DNA and.