It yields considerable changes in shape of derivative achieved. Shown on the left are the fourth derivative spectra for phenylalanine and tyrosine.

Appropriate selection of derivative order gives useful separation of overlapped signals.
Second derivative uv spectroscopy. The second derivative spectroscopy method requires the use of a UVVisible scanning spectrophotometer. This instrument has a large up-front cost but requires minimal future maintenance. The method is simpler and much faster than many other methods as spectrophotometric analysis takes approximately 1 min per sample.
The purpose of this study was to examine the accuracy and. A method for nitrate analysis based on second derivative UVVisible spectroscopy was developed by Simal et al. Simal J Lage M.
A and Iglesias I. 1985 Second derivative ultraviolet spectroscopy and sulfamic acid method for determination of nitrates in water. HOW IS SECOND DERIVATIVE UV ANALYSIS BEING IMPLEMENTED AT ALTHEA Early phase analytics Characterization of reference standard Can be used for rapid in-process analysis to verify consistent protein conformation Can be used to support method development protein peak ID peak purity.
Second derivative ultraviolet UV spectroscopy is used for the identification and quantitation of nitrates in water with satisfactory precision and accuracy. Nitrite interference is eliminated with sulfamic acid. Interference from organic matter can be cancelled with the use of second derivative UV spectroscopy.
These shifts are best measured using either the second or fourth derivative of the zero order UV spectra. Shown on the left are the fourth derivative spectra for phenylalanine and tyrosine. What stands out in these spectra is the wealth of additional information they provide over the zero order spectra.
Each derivative spectrum has a number of minima and maxima bands. It is the wavelengths of these bands. A method for nitrate analysis based on second derivative UVVisible spectroscopy was developed by Simal et al.
Simal J Lage M. A and Iglesias I. 1985 Second derivative ultraviolet spectroscopy and sulfamic acid method for determination of nitrates in water.
68 962-964 and Suzuki and Kuroda 1987. 1987 Direct simultaneous determination of nitrate. Second derivative spectroscopy is a means to extract information from the spectrum.
In contrast to the relatively featureless UV spectra the second derivatives of UV spectra are characterized by two sharp peaks and troughs. Derivative spectroscopy accomplishes conversion of a normal or zero order spectrums to its first second or higher derivative spectrum. It yields considerable changes in shape of derivative achieved.
Appropriate selection of derivative order gives useful separation of overlapped signals. Criterion like signals height their width and distance between maxima in basic spectrum is achieved by optimal. First second third and fourth order derivative spectra can be calculated.
The Derivative functions calculate the derivative of the data points y-values in the spectrum to the specified derivative order using a Savitsky-Golay algorithm with a filter length of 5 and a polynomial degree of 3. For a complete description of the Derivative function Derivative on page 18. It involves the conversion of a normal spectrum to its firstsecond or higher derivative spectrum.
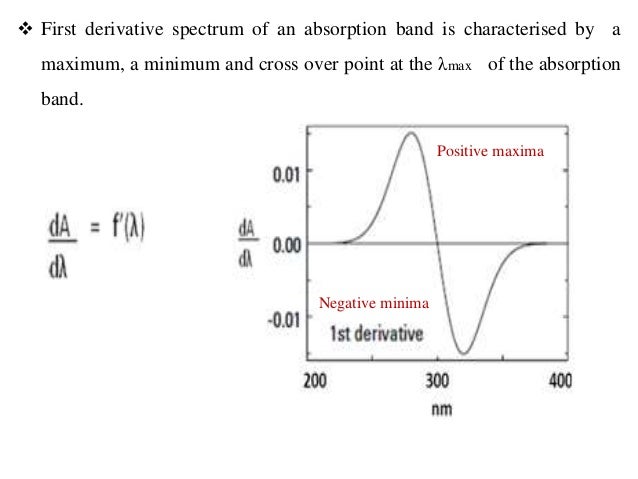
The normal absorption spectrum is reffered to as the fundamental zero order or D0 spectrum. The first derivative D1 spectrum is a plot of the rate of change of absorbance with wavelength against wavelength dAdʎ The second derivative spectrum is a plot of the curvature of the D0 spectrum against wavelength or a plot of d2Adʎ2 ʎ. Second-derivative spectroscopy has proven to be an effective analytical tool because of its ability to resolve overlapping bands in the normal spectrumThis protocol is.
Derivative spectrophotometry is a technique whic h is based on derivative spectra of a basic zero-order spectrum. The results of derivatisation of function described a run of absorbance curve is called the derivative sp ectrum and can be expressed as. N D xÌd n Ad Ìn f Ì or n D xÎ d n Ad Î n f Î.
What Is Derivative spectroscopy. It is a simplest method for an increasing a selectivity is derivatisation of spectra. This operation allows to remove spectral interferences and as a consequence leads to increase selectivity of assay.
Derivative spectroscopy involves the conversion of a normal spectra to its first second or higher derivative spectra. The normal spectrum is known as fundamental. By second-derivative UV spectroscopy.
Total N and organic N are determined based on second- derivative analyses of NO- following persulfate digestion. Resolution of organic N determina- tions was increased by using ion-exchange resins to remove NO- from samples with high con- centrations of N03- prior to persulfate oxidation. Second derivative spectroscopy is a technique which enhances the separation of overlapping peaks.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the specificity of the second derivative peaks for the main tissue components of articular cartilage AC ie collagen and proteoglycans PGs. Other works have presented the second derivative UV-Vis spectroscopy absorption spectrum for NO 3 N calibration. There are continuous sensors and analyzers capable of operating online with UV.
Second-derivative UV absorbance spectroscopy may be also used to determine pK a of Tyr side-chains in proteins Breydo et al. The method monitors the decrease in intensity of the second-derivative of the spectrum at the isosbestic point corresponding to the transition between buried and exposed non-ionized Tyr residues 2842 nm. Existence of the isosbestic point see an example in Fig.
The UV first and second derivative spectra for paliperidone were recorded at the wavelength of 279nm 248nm 246 nm respectively Figure3 Figure 5 and Figure 7. The proposed method was found that the drug obeys linearity with in concentration range of 2-10gml Table 1 Table 2 and Table 3 and Figure 2 Figure 4 and Figure 6.