
Specialised Transduction - The only bacterial genes that can be transduced are very near to the site at which pro phage is integrated. Specialized transduction is the process by which a restricted set of bacterial genes are transferred to another bacterium.
The prophage undergoes replication along with bacterial genome replication.
Specialised transduction in bacteria. Transduction has been found to occur in a variety of bacterial populations including. Escherichia coli Pseudomonas spp Salmonella spp Staphylococcus spp. Specialized Transduction Specialized transduction can occur only through the lysogenic cycle ie.
Here only the specific part of the bacterial DNA is packed into the virus. It occurs when the prophage ie. Viral DNA which gets inserted into the bacterial genome in the lysogenic cycle excises.
Specialised transduction is mediated by lysogenic phages. Here specific DNA fragment are integrated into the host chromosome. Here phage DNA gets integrated with the bacterial chromosome viral genome integrated into the bacterial genome is called prophage.
The prophage undergoes replication along with bacterial genome replication. In specialized transduction bacteriophage transfer only a few restricted gene DNA fragments from donor bacteria to. At first temperate bacteriophage enter into donor bacteria and then its genome gets integrated with host cells DNA at.
When such lysogenic cell is. In specialized transduction the phage undergoes lysogeny usually at specific locations in the bacterial genome called attachment sites. During this process the phage genome usually integrates into the bacterial.
Bacterial transduction or simply transduction is a type of gene transfer where a bacterium transfers its DNA or a portion of it to another bacterium that is not its offspring by using a virus as a vectorUnlike other processes of gene transfer like horizontal gene transfer and conjugation transduction does not require the physical contact between the host cell and the cell that will. Specialised Transduction - The only bacterial genes that can be transduced are very near to the site at which pro phage is integrated. The only site at which λ phage integrated is between genes for galactose fragmentation gal gene and biotin biosynthesis gene.
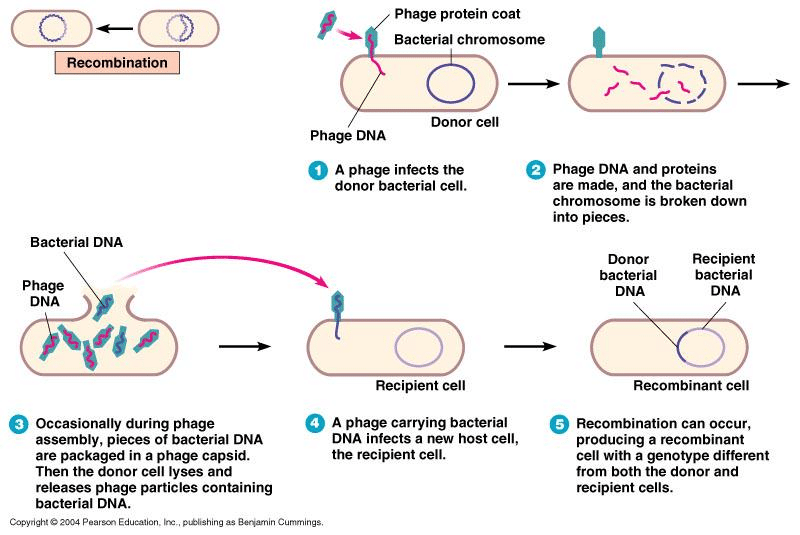
Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages which literally translates to bacteria-eater Sometimes instead of just infecting and hijacking the host the virus picks up and transfers. This transfer of bacterial genes adjacent to prophage only to the recipient chromosome is called restricted or specialized transduction Fig. For the first time Morse 1956 discovered specialized transduction.
It is made possible by an error in the lysogenic life cycle of phage. Specialized transduction is the process by which a restricted set of bacterial genes are transferred to another bacterium. The genes that get transferred donor genes depend on where the phage genome is located on the chromosome.
Specialized Transduction In specialized or restricted transduction the transducing particle carries only specific portions of the bacterial genome Specialized transduction is made possible by an error in the lysogenic life cycle. In this type of transduction a specific segment of the bacterial genetic material is packed along with the viral genome. This kind of transduction occurs only through the lysogenic life-cycle.
The prophage can be used for being integrated into the bacterial chromosome in a targeted manner. Specialized transduction. A DNA fragment is transferred from one bacterium to another by a temperate bacteriophage that is now carrying donor bacterial DNA due to an error in spontaneous induction during the lysogenic life cycle.
In specialized transduction the phage inserts its genome at the specific site. In specialized transduction a only bacterial genes near the site of integration of the phage DNA can be transduced. B any random bacterial gene can be transduced.
C only genes on. Specialized Transduction Specialized transduction can only occur with temperate bacteriophage since it involves the lysogenic cycle of replication. The bacteriophage randomly attaches to a bacterial host cell injecting viral DNA inside.
The DNA integrates into the chromosome of the host cell forming a prophage.