
Across-sectional area of the bar m 2 shearing stress P a. Torsion Formula for Thin Walled Tubes.
Bending of Beam Elementary Cases 11 6.
Strength of materials formulas. Strength of Material Formula Short Notes fStress and strain Stress Force Area L Changeinlength Tension strain et L Initial length fBrinell Hardness Number BHN D P D D2 d 2 2 where P Standard load D Diameter of steel ball and d Diameter of the indent. Where Y S is the Yield Strength and D S is the Design Stress. See our Material Terms and Links page for additional information.
Strength of Materials Area Moment Methods to Calculate Deflection in Beams Material Specifications and Characteristics - Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Pinned Columns and Buckling Moment of Inertia Section Modulus Radii of Gyration Equations Triangular Hex. Strength of Materials Equation Sheet Strength of Materials Equation Sheet 1 p M El My P My M z My M z My IMI 1 rpm Hz filb in 1b lhp 550 6600 Irad 5729 AE cos2 cos 9 sin 9 A td. In mechanics of materials the strength of a material is its ability to withstand an applied load without failure or plastic deformationStrength of materials basically considers the relationship between the external loads applied to a material and the resulting deformation or change in material dimensions.
In designing structures and machines it is important to consider these factors in. Strength of Materials. Torsion Formula for Thin Walled Tubes.
Torsion Formula for Circular Shaft. Total elongation in a material which hangs vertically under its own weight. Wweight of the material.
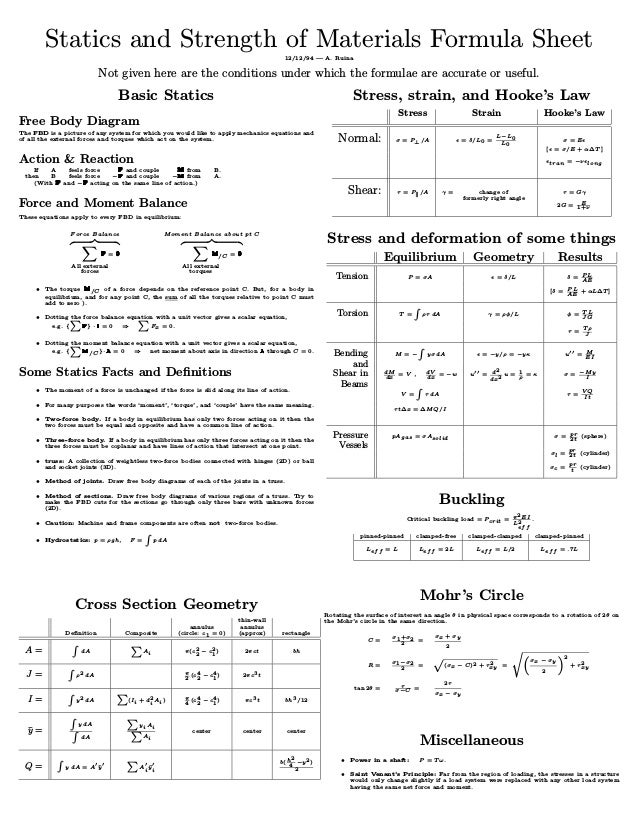
Torsion formula for Thin walled tubes. Where maximum shearing stress P a Shearing stress at. Statics and Strength of Materials Formula Sheet 121294 A.
Ruina Not given here are the conditions under which the formulae are accurate or useful. Basic Statics Free Body Diagram The FBD is a picture of any system for which you would like to apply mechanics equations and of all the external forces and torques which act on the system. Mechanics of materials or strength of materials is central to the whole activity of engineering design.
Usually the objectives in analysis here will be the determination of the stresses strains and deflections produced by loads. Adequate summary of the formulas facts and principles pertaining to strength of materials. It is intended primarily as a reference book and represents an attempt to meet what is believed to be a present need of the designing engineer.
This need results from the necessity for more accurate methods of. Of a single material. The centroid and then the moment of inertia are found on the transformed section for use in the bending stress equations.
COMPOSITE SECTION MATERIAL 1 MATERIAL 2 E 1 A 1 E 2 A 2 b E 2 A 2 E 2 nA 1 TRANSFORMED SECTION b nb NEUTRAL AXIS COLUMNS Critical axial load for long column subject to buckling. Eulers Formula P K. IMPORTANT 1000 GATE CIVIL ENGINEERING FORMULAS TOPIC WISE PDF We already know cracking of GATE exam is not easiest one.
If we want to crack GATE exam we need hard and smart work. Here below we have shared the important 1000 formulas topic wise which are very useful to our GATE civil engineering examination. Strength Of Materials.
Strength of materials also called Mechanics of materials is a subject which deals with the behavior of solid objects subject to stresses and strains. The study of strength of materials often refers to various methods of calculating the stresses and strains in structural members such as beams columns and shafts. Strength of Materials The following are basic definitions and equations used to calculate the strength of materials.
Stress is the ratio of applied load to the cross-sectional area of an element in tension and is expressed in pounds per square inch psi or kgmm 2. Strength of Materials Formulas Stress. Where σnormal stress or tensile stress p a.
Pforce applied N. Across-sectional area of the bar m 2 shearing stress P a. Astotal area in shear m 2.
Where tensile or compressive strain mm. Strength of Material Formula Short Notes Stress and strain Stress Force Area t L Changeinlength Tensionstrain e L Initial length Brinell Hardness Number BHN 22 2 P D D D d S where P Standard load D Diameter of steel ball and d Diameter of the indent. Strength of Materials also known as Mechanics of Materials and Mechanics of Deformable Bodies is the study of the internal effect of external forces applied to structural member.
Stress strain deformation deflection torsion flexure shear diagram and moment diagram are some of. Stress Strain and Material Relations 2 3. Geometric Properties of Cross-Sectional Area 3 4.
One-Dimensional Bodies bars axles beams 5 5. Bending of Beam Elementary Cases 11 6. Material Fatigue 14 7.
Multi-Axial Stress States 17 8. Energy Methods the Castigliano Theorem 20 9. Stress Concentration 21 10.
Material data 25 Version 03-09-18.