Thermal conductivity can be defined as the quantity of heat transmitted through a unit thickness of a material - in a direction normal to a surface of unit area - due to a unit temperature gradient under steady state conditions. WKm or in IP units Btuhr1ft1F1 ie.

The constant of proportionally λ is the thermal conductivity.
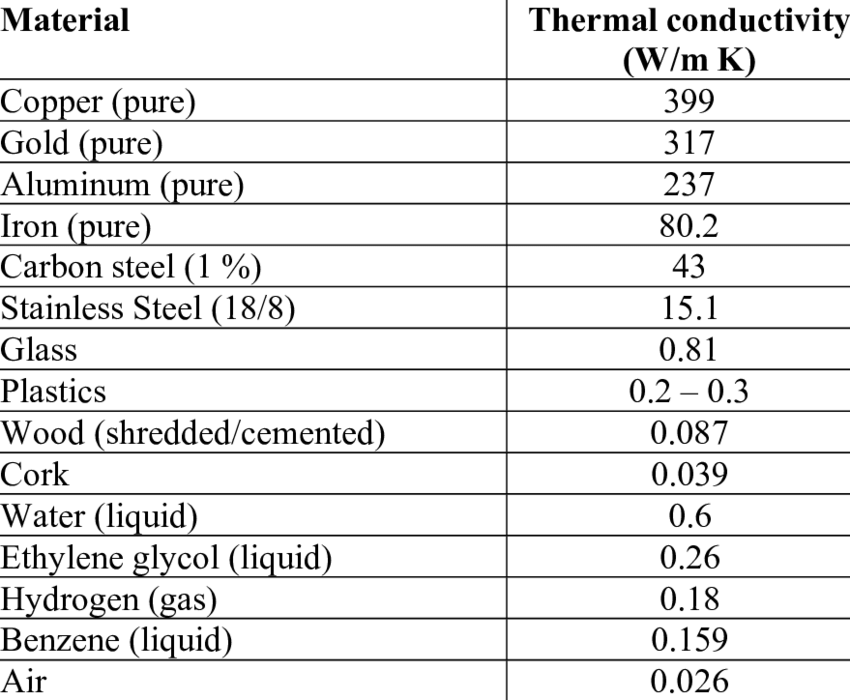
Thermal conductivity constant table. Thermal conductivity calseccm 2 Ccm Thermal conductivity Wm K Diamond. Water at 20 C. 134 rânduri The plate distance is one centimeter the special conductivity values were calculated.
3145 Thermal conductivity coefficient. The following table gives values of conductivity for solids liquids and gases. Thermal conductivity coefficients W m.
Thermal conducTiViTy of gases marcia l. Huber and allan h. Harvey The following table gives the thermal conductivity of some common gases as a function of temperature.
Unless otherwise noted the thermal conductivity values refer to a pressure of 100 kPa 1 bar or to the saturation vapor pressure if that is less than 100 kPa. 293 rânduri Thermal conductivity is a material property that describes ability to conduct heat. The basic law of thermal conduction is the Fourier law which states that the heat flux density is proportional to the temperature gradient T in an isotropic body.
The constant of proportionally λ is the thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity can be defined as the quantity of heat transmitted through a unit thickness of a material - in a direction normal to a surface of unit area - due to a unit temperature gradient under steady state conditions. Thermal conductivity most common units are W m K in the SI system and Btu h ft F in the Imperial system.
10 6 kgs m MPa s. Surface tension kgs 2 Nm. Specific entropy of vaporization.
Ie conduction occurs in the direction of decreasing temperature and the minus sign confirms this thermodynamic axiom and the proportionality constant k is the Thermal Conductivity of the material WmK. Fouriers Law thus provides the definition of thermal conductivity and forms the basis of many methods of determining its value. 26 rânduri Heat Transfer Table of Content Properties of Metals - Thermal Conductivity Density.
The general conduction formula for thermal impedance for a given material is. K ACS L θ 1 Where K is the Thermal Conductivity Factor L is the thermal path length ACS is the cross sectional area where the heat is being applied A low theta is desired since this is the temperature rise in C per Watt of heat dissipated. Molar heat capacity gases.
Melting points Heat of fusion. Boiling points Heat of vaporization. In heat transfer analysis thermal diffusivity is the thermal conductivity divided by density and specific heat capacity at constant pressure.
It measures the rate of transfer of heat of a material from the hot side to the cold side. It has the SI unit of m²s. Updated June 27 2019.
This table presents the electrical resistivity and electrical conductivity of several materials. Electrical resistivity represented by the Greek letter ρ rho is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. 23 Nitrogen Nitrogen gas was introduced from the tank directly into the thermal conductivity apparatus.
The thermal conductivities of nitrogen gas were determined for 1 X 105 and 101 107 Pa pressure at 960 c and for 1 X 105 101 X 107 and 253 X 107 Pa pressure at 75C. Thermal conductivity 1 Thermal conductivity In physics thermal conductivity is the property of a materials ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fouriers Law for heat conduction.
Thermal conductivity is measured in watts per kelvin-meter WK1m1 ie. WKm or in IP units Btuhr1ft1F1 ie. Multiplied by a temperature difference in kelvins K.