They are generally labeled with a Warning or Caution Because the neonicotinoid pesticides block specific neurons in insects they are deemed less harmful to warm-blooded animals but are highly toxic to insect pests as well as beneficial species like bees. Other concerns such as sub-lethal effects impacts to solitary pollinators metabolites degradants synergistic effects and accumulation in biota are.

The name literally means new nicotine-like insecticides.
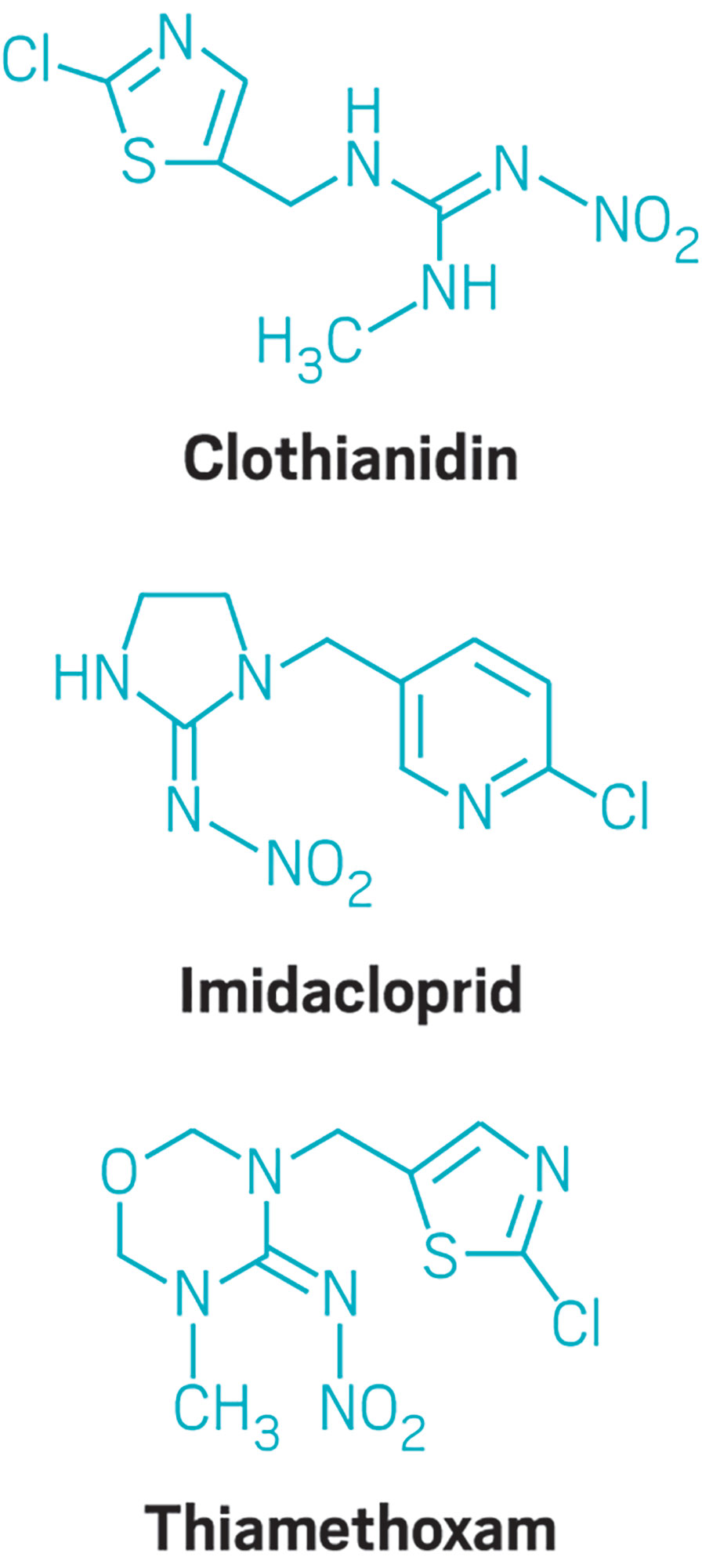
What are neonicotinoid pesticides. Neonicotinoids are a new class of insecticides chemically related to nicotine. The name literally means new nicotine-like insecticides. Like nicotine the neonicotinoids act on certain kinds of receptors in the nerve synapse.
They are much more toxic to invertebrates like insects than they are to mammals birds and other higher organisms. Neonicotinoids are a new class of insecticides. They act as agonists at the insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptor Na K ionophore affecting initiation of the electric signal in the postsynaptic neuron.
Their toxicity to mammals and other vertebrates is low because of the distinct features of the target receptor sites in insects. Neonicotinoid pesticides are a class of chemicals that act as insecticides by exerting neurotoxic effects via irreversible binding to insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. The EPA classifies neonicotinoids as both toxicity class II and class III agents.
They are generally labeled with a Warning or Caution Because the neonicotinoid pesticides block specific neurons in insects they are deemed less harmful to warm-blooded animals but are highly toxic to insect pests as well as beneficial species like bees. January 30 2020 EPA is taking the next step in its regulatory review of neonicotinoid pesticides - a group of insecticides used on a wide variety of crops turf ornamentals pets for flea treatment and other residential and commercial indoor and outdoor uses. Neonicotinoids are a group of insecticides that are used widely on farms as well as around our homes schools and city landscapes.
Used to protect against sap-sucking and leaf-chewing insects neonicotinoids are systemic which means they are absorbed by the plant tissues and expressed in all parts including nectar and pollen. Pesticides are both used on farms and ones commonly sold to homeowners. The most damaging are the neonicotinoids that destroy butterflies bees bumblebees pollinators and birds.
Neonicotinoids are a class of insecticides commonly used in agriculture and increasingly associated with declines in bee populations and bee viability is an important concern given the utility. Neonicotinoid Pesticides are a new class of neuroactive insecticides that are chemically related to nicotine. They are more toxic to insects than they are to larger animals such as mammals and birds.
The popularity of neonicotinoid pesticides in pest control has surged due to their high water solubility. The US Environmental Protection Agency EPA recently banned 12 products containing neonicotinoid a pesticide that functions similarly to nicotine. Neonicotinoid insecticides are now the most widely used class of insecticides in the world.
While they were initially introduced as less harmful than older insecticides research has now shown their devastating ecological impacts. Neonicotinoids are very toxic to pollinators beneficial insects and aquatic invertebrates. Their widespread use combined with their water solubility means that.
While many studies had connected neonicotinoids a common class of insecticides derived from nicotine to bee deaths in the past few studies had examined how much pesticide is needed to harm. In 2012 the European Food Safety Authority the leading pesticide regulator in the EU released a risk assessment finding that the three most widely used neonicotinoids. Pesticides Neonicotinoids also referred to as neonics are insecticides derived from nicotine.
They act by binding strongly to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system of insects causing overstimulation of their nerve cells paralysis and death. Health neonicotinoid pesticides and address ongoing and possible future work to decrease pollinator exposure to pesticides in Vermont. Other concerns such as sub-lethal effects impacts to solitary pollinators metabolites degradants synergistic effects and accumulation in biota are.
Neonicotinoids introduced in the late 1980s were supposed to be a safer alternative to previous insecticides. But study after study has found that they play a key role in insect decline.