
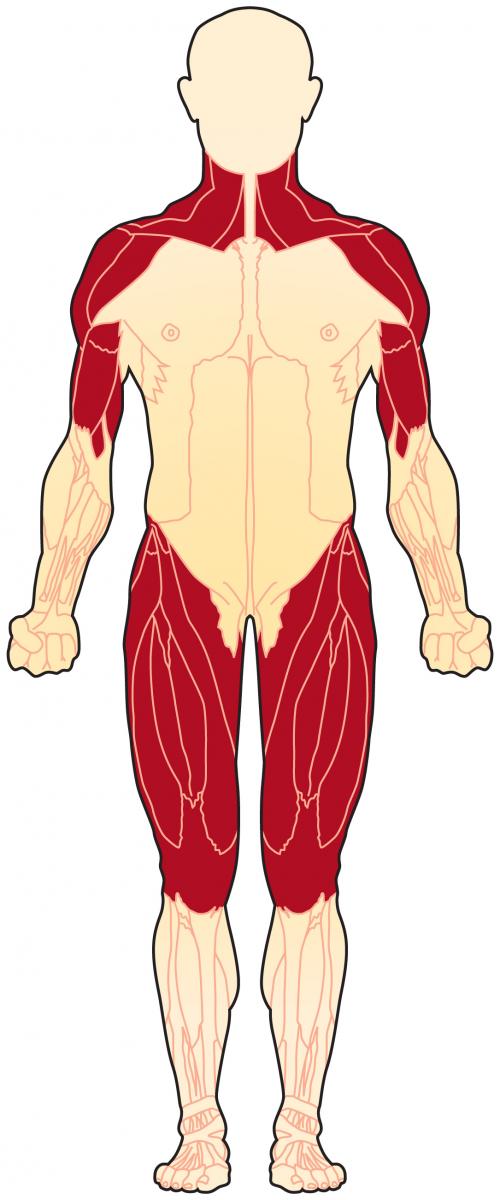
Common symptoms reported by people with proximal myopathy. Great as weakness of more proximal closer to the body muscles controlling the pelvic or shoulder girdles which hold large components of the total body mass against the force of gravity.
Skin layer with red circle indicating region of proximal hamstring tendons.
What are proximal muscles. Great as weakness of more proximal closer to the body muscles controlling the pelvic or shoulder girdles which hold large components of the total body mass against the force of gravity. Weakness of the proximal muscles that control the shoulder blade scapula for example results in winging ie when the Read More. Proximal muscles are those muscles that are closest to the core of your body including the upper legs hips upper arms shoulders and the core itself.
The main causes of muscular proximal weakness are. Guillain-Barre syndrome and other polyneuropathies. Proximal forms of progressive spinal.
Weakness of the proximal muscles those muscles that are closest to the core of your body including in the arms and shoulders can be a symptom in several muscle diseases. For example in the disease polymyositis weakness in arms and weak shoulders as well as weakness in the hips and thighs can appear over a period of weeks or months. This patient has a lipid-storage myopathy with massive accumulation of lipids in muscle fibres which can develop in primary carnitine deficiency multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency MADD or neutral lipid storage disease.
These diseases commonly manifest as progressive proximal muscle weakness rather than as episodic exercise intolerance. Pattern of weakness in myopathy most commonly tends to involve proximal upper andor lower limb muscles in a symmetrical fashion hence the prefix proximal. Myopathy can also less commonly involve distal limb neck facial ocular pharyngeal respiratory and cardiac musculature.
Proximal myopathy is a condition that involves muscle weakness muscle loss muscle inflammation and muscle pain. Common symptoms reported by people with proximal myopathy. This muscle is the most anterior and medial of all four anterior leg muscles.
It originates from the proximal portion of the leg precisely from the lateral tibial condyle and proximal half of the tibial shaft in addition to the adjacent portion of the interosseous membrane. The muscles most affected are those closest to the body proximal muscles specifically the muscles of the shoulders upper arms pelvic area and thighsThe severity age of onset and features of limb-girdle muscle dystrophy vary among the many subtypes of this condition and may be inconsistent even within the same family. The proximal end of the femur connects to the hip joint.
It is marked by a spherical ball called the femoral head that fits into the socket of the hip joint the acetabulum. It is marked by two large articular processes called condyles which sit on top of the tibia. Part 6 - Proximal leg muscles - YouTube.
Corine and Marsha explain the upper leg muscles required for BIO244 at CLC. Corine and Marsha explain the upper leg muscles required for BIO244 at. Proximal upper limb UL muscle function measured by the 1 kg arm lift test and lower limb LL muscle function measured by the 30 s chair stand test in 30 control subjects.
The UL score is the mean of the number of 1 kg arm lift repetitions performed in 30 s in both arms. The proximal hamstring tendons are the tendons at the top proximal means closer to the head of the hamstring muscles in the back of the thigh. These tendons join the hamstring muscles onto the sitting bones ischial tuberosities.
Back view of body. Skin layer with red circle indicating region of proximal hamstring tendons. Corine and Marsha explain the upper arm muscles including origins insertions and actions required for BIO244 at CLC.
These are terms implying the location of something in relation to something else. We use it to describe if something is closer or further away either from a certain specific area or from the general center of the body. For example your hand is dis.
Posterior surface of entire humeral shaft. Posterior surface of proximal end of humerus. Inferior margin of glenoid cavity and joint capsule.