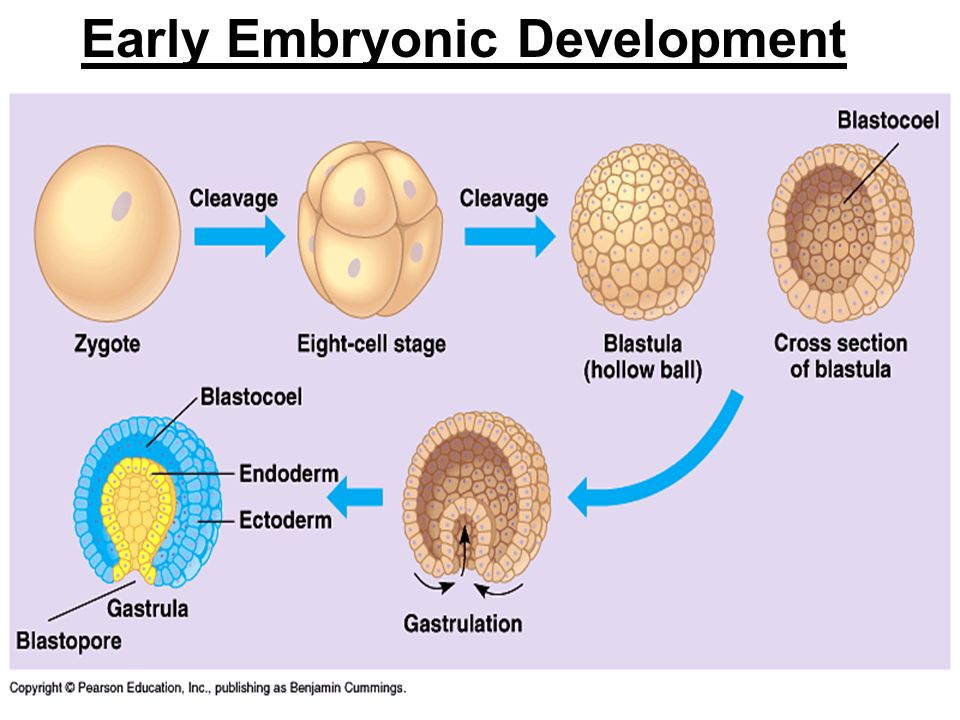
The initial growth stages of multi-cellular organisms start with a zygote cell which then undergoes fast cell division to form the initial cell cluster or blastula. They occur via four essential stages in early animal development.
In animals one can usually distinguish 4 stages of embryonic development.
What are the stages of embryonic development in animals. They occur via four essential stages in early animal development. The process of a single sperm cell combining with single egg cell to form a zygote. Rapid multiple rounds of mitotic cell division where the overall size of the embryo does not increase.
The developing embryo is called a blastula following completion of cleavage. What are the Stages of Embryonic Development. Name the 5 major stages of embryonic development and explain why each stage is a significant milestone in development of animals.
Regarding embryonic cleavage and blastula formation. Compare the rate of cell division at these stages indicate how yolk affects these stages in amphibians and birds. The initial growth stages of multi-cellular organisms start with a zygote cell which then undergoes fast cell division to form the initial cell cluster or blastula.
This rapid division of cells. In animals the zygote progresses through a series of developmental stages during which primary germ layers ectoderm endoderm and mesoderm are established and reorganize to form an embryo. During this process animal tissues begin to specialize and organize into organs and organ systems determining their future morphology and physiology.
There are two main types of cellular development that pertain to embryos. Mosaic development or regulative development. In mosaic development which is not characteristic of mammals but of organisms such as annelids differentiation occurs in steps that are set in order and progression without input occurring between neighboring cells.
Animals Embryology Embryos Normal Stages of Embryos Development Fate of the Neural Crest Cells Ectodermal Organs Embryology Maturation of the Egg Oogenesis Gametogenesis Embryology. In mammals the blastula forms the blastocyst in the next stage of development. Here the cells in the blastula arrange themselves in two layers.
The inner cell mass and an outer layer called the trophoblast. The inner cell mass is also known as the embryoblast. This mass of cells will go on to form the embryo.
Clicking the Carnegie stage numbers opens a page dedicated to describing that single stage and the associated developmental events. This page shows some key events of human development during the embryonic period of the first eight weeks weeks 1 - 8 following fertilization. This period is also considered the organogenic period when most organs.
Name the 5 major stages of embryonic development and explain why each stage is a significant milestone in development of animals. Regarding embryonic cleavage and blastula formation. Compare the rate of cell division at these stages.
Indicate how yolk affects these stages in amphibians and birds. Draw the blastula stage of a sea urchin. Author of An Introduction to Embryology.
Animal development the processes that lead eventually to the formation of a new animal starting from cells derived from one or more parent individuals. Development thus occurs following the process by which a new generation of organisms is produced by the parent generation. In animals one can usually distinguish 4 stages of embryonic development.
Cleavage Patterning Differentiation Growth. Mitosis and cytokinesis of the zygote an unusually large cell produces an increasing number of smaller cells each with. After fertilization a series of developmental stages occur during which primary germ layers are established and reorganize to form an embryo.
During this process animal tissues begin to specialize and organize into organs and organ systems determining their. In developmental biology embryonic development also known as embryogenesis is the development of an animal or plant embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell by a sperm cell.
Once fertilized the ovum becomes a single diploid cell known as a zygote. The zygote undergoes mitotic divisions with no significant growth and cellular differentiation leading to development. Embryo development in mammals begins at fertilization with migration and fusion of the gametic pronuclei and extensive genome-wide epigenetic remodeling.
The hallmark of preimplantation development is the transition from gametic to embryonic differentiation programs. At this stage of development illustrated in Figure 2425 the inner cell mass consists of embryonic stem cells that will differentiate into the different cell types needed by the organism. The trophoblast will contribute to the placenta and nourish the embryo.
Name the 5 major stages of embryonic development and explain why each stage is a significant milestone in development of animals. Fertilization Fusion of sperm and egg 2.
