It does so with regions of specific amino. Our video takes the viewer on an educational journey about integral proteins.

The Fluid Mosaic Model.
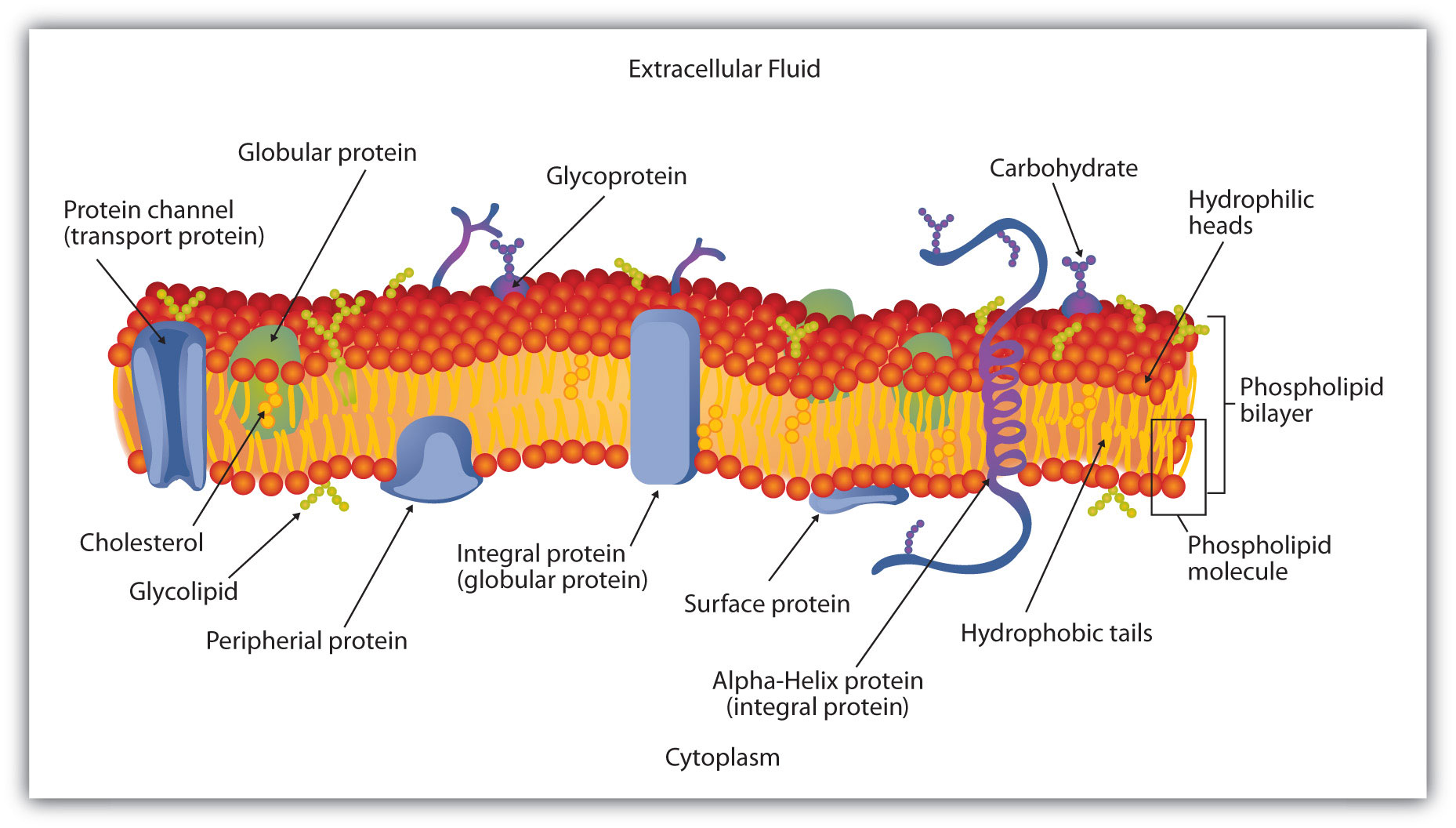
What do integral proteins do. Integral Protein Definition. An integral protein sometimes referred to as an integral membrane protein is any protein which has a special functional region for the purpose of securing its position within the cellular membrane. In other words an integral protein locks itself into the cellular membrane.
It does so with regions of specific amino. Carrier proteins and channel proteins are some of the integral proteins. Their main function is to allow the polar and big molecules to pass across the membrane which are restricted by the phospholipid bilayer.
They act as the gate for making the transportation either active or. Integral proteins contain both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts. Peripheral proteins contain hydrophilic parts.
Integral proteins serve as carrier proteins channel proteins and enzymes. Peripheral proteins serve as receptors and surface antigens. Integral membrane proteins may penetrate the membrane partially or may exist as transmembrane proteins interfacing with both the cytosol and external environment.
They interact strongly with the membrane lipids through hydrophobic side chains of amino acids and can only be removed by destroying membrane structure with detergent or solvent. The functions can vary greatly the fact that its an integral protein limits the functions but there are still many different functions. Ill go through a few functions of integral transmembrane.
Examples of integral proteins are membrane bounded enzymes drug and hormone receptors antigen and rhodopsin. Integral proteins represent around 70 while peripheral proteins represent the remaining portion of plasma membrane proteins. Our video takes the viewer on an educational journey about integral proteins.
The structure of a phospholipid includes a hydrophillic or water loving phosp. An integral membrane protein also known as an IMP is one which spans the entire biological membrane of a cell. These proteins are attached permanently to the cell membrane and their function typically relies on being present in the membrane.
Both structurally and functionally they are integral parts of the membranes of cells. These proteins transfer electrons from integral proteins they are attached to and can pass the electrons to other proteins and molecules. Effectively this stores the energy from the breakdown of the products of glycolysis into easily accessible molecules or ATP.
What are Transport Proteins and What Do they Do Transport proteins or transporter are integral membrane proteins that help other substances to diffuse in and out of the cell. They are similar to cell receptors in some ways. Both are transmembrane proteins that transport signals from outside the cell to.
Integral proteins act as ion channels ion pumps and structural support. The peripheral proteins act as cell identity markers. What is the longest and shortest bone in the human body.
What are their measurements in inches. The longest bone is the Femur thigh bone and the shortest one is the Stapes one of the 3 small bones inside the ear. Functions of the integral proteins.
Making transport channels for small dissolved ions. Acting as enzymes for the active transport of materials into the cell against a concentration gradient. Many integral membrane proteins serve as cytoskeleton anchors to the plasma membrane.
These include adhesion molecules as well as ion channels pumps cotransporters and exchangers Denker and Barber 2002. Such interactions are critical for the stability and. Integral proteins act as ion channels ion pumps and structural support.
The peripheral proteins act as cell identity markers. Structure of a cell membrane. Proteins of the cell membrane is divided into two groups.
Integral proteins directly incorporated within the lipid bi-layer and Peripheral proteins loosely associated with membrane surface. Integral proteins act as ion channels ion pumps and structural support. The peripheral proteins act as cell identity markers.
Structure of a cell membrane. Proteins of the cell membrane is divided into two groups. Integral proteins directly incorporated within the lipid bi-layer and Peripheral proteins loosely associated with membrane surface.
Functions of the. The Fluid Mosaic Model. Nicolson proposed the now widely accepted Fluid Mosaic Modelof the structure of cell membranesThe model proposes that integral membrane proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer as seen in Figure aboveSome of these proteins extend all the way through the bilayer and some only partially across it.