
If P purple and p white what is the genotypic ratio for the F 1 generation that results from a cross between PP and P p. Each is now its own chromosome.
We hope you get all your answers here.
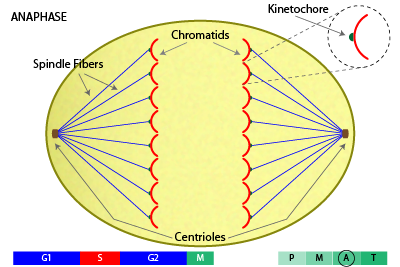
What happens to the sister chromatids during anaphase. In anaphase the sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell. The protein glue that holds the sister chromatids together is broken down allowing them to separate. Each is now its own chromosome.
What happens to the sister chromatids during -Anaphase I of meiosis -Anaphase II of meiosis 22. At the end of meiosis II each of the four resulting cells gametes contain how many chromosomes. If P purple and p white what is the genotypic ratio for the F 1 generation that results from a cross between PP and P p.
Complete the Punnett square below. In anaphase sister chromatids separate and begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell. Once the paired sister chromatids separate from one another each chromatid is considered a single-stranded full chromosome.
In telophase and cytokinesis separated sister chromatids are divided into two separate daughter cells. In anaphase the chromatids separate and are pulled by the microtubules to opposite ends of the cell. During anaphase sister chromatids or homologous chromosomes for meiosis I will separate and move to opposite poles of the cell pulled by microtubules.
The sister chromatids are pairs of identical copies of DNA joined at a point called the centromere. During anaphase each pair of chromosomes is separated into two identical independent chromosomes. The separated chromosomes are then pulled by the spindle to opposite poles of the cell.
Click to see full answer. What happens to sister chromatids during anaphase. They chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell.
What pulls sister chromatids apart during anaphase. What happens during anaphase 1 and anaphase 2. Generally anaphase I involve separating the chromosomes from each sister chromatid to the opposite poles still attached to the microtubules of the cell while anaphase 2 involves the actual split of the sister chromatids into single chromatids.
1 If sister chromatids do not split equally during anaphase of mitosis one daughter cell would have more chromosomes than normal and one daughter cell would have fewer. During mitosis sister chromatids separate from each other during anaphase. This will occur when the spindle fibres attached to each chromosome shorten causing the double-stranded chromosome to.
Anaphase is a very important stage of cell division. It ensures that duplicated chromosomes or sister chromatids separate into two equal sets. Each set of chromosomes will become part of a new cell.
If chromosomes fail to separate properly during anaphase nondisjunction. In anaphase I the homologous chromosomes are separated. In prometaphase II microtubules attach to the kinetochores of sister chromatids and the sister chromatids are arranged at the midpoint of the cells in metaphase II.
In anaphase II the sister chromatids are separated. Telophase II and Cytokinesis. Sister chromatids are pulled apart by spindle fibers and move toward opposite ends of the cell is correct for What happens during the mitotic phase anaphase.
Thankyou for using answerout. We hope you get all your answers here. If you have any special questions you can comment to ask us.
The primary difference is that in meiosis II only one member of each homolog pair is present whereas in mitosis both are. During anaphase II the third step of meiosis II the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move toward opposite poles. Once they are no longer connected the former chromatids are called unreplicated chromosomes.
Anaphase begins when the duplicated centromeres of each pair of sister chromatids separate and the now-daughter chromosomes begin moving toward opposite poles of the cell due to the action of the spindle. At the end of anaphase a complete set of chromosomes has assembled at each pole of the cell. During anaphase II the third step of meiosis II the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move toward opposite poles.
Once they are no longer connected the former chromatids are called unreplicated chromosomes. How many chromosomes are in each stage of meiosis. What happens during anaphase Each sister chromatid of a chromosome has spindle fibers attached to it.
These spindle fibers begin to shorten and pull the sister chromatids apart at the centromere. The chromosomes during anaphase usually have a distinct V shape. The separase triggers the cleavage of cohesin the protein complex that binds sister chromatids together.
During metaphase sister chromatids are linked by intact cohesin complexes. When securin undergoes ubiquitination by the APCC and releases separase which degrades cohesin sister chromatids become free to move to opposite poles for anaphase.