Each spring can be deformed stretched or compressed to some extent. Since k is a constant the relationship between force and distance is linear.
This video introduces the Spring Force as used in Physics.
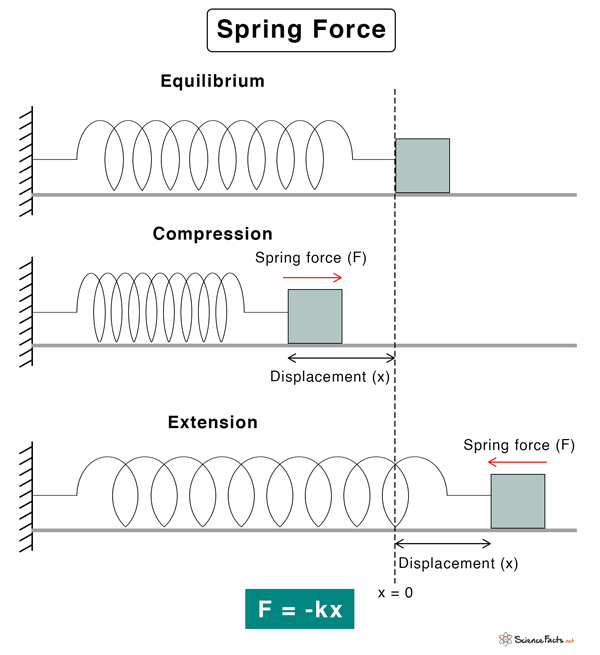
What is a spring force. What is Spring Force. When a metal spring is stretched or compressed it is displaced from its equilibrium position. As a result it experiences a restoring force that tends to retract the spring back to its original position.
This force is called the spring force. It is a contact force that can be found in elastic materials. This fact tells us that spring exerts an equal as well as an opposite force on a body which compresses or stretches it.
The Spring force formula is given by F kx x 0 Where the spring force is F the equilibrium position is x o the displacement of the spring from its. Simple harmonic oscillationsthe force is called the spring force. If x is positive displacement to the right the resulting force is negative to the left and vice versa.
In other words the spring force always acts so as to restore mass back toward its equilibrium position. Spring force is the description of the force that causes the spring to rebound. It is a characteristic of the material at a molecular level and its three-dimensional shape on a macro level.
Hookes law is the customary formula for calculating this force. Constant pressure on a surface may be all that is required of a spring in a mechanism. The spring force is F the equilibrium position is x o the displacement of the spring from its position at equilibrium is x the spring constant is k.
For a given spring and other elastic objects the extension is directly proportional to the force applied. Since k is a constant the relationship between force and distance is linear. A higher spring constant means a stiffer spring thats harder to stretch because for a given displacement x the resulting force F will be higher while a looser spring thats easier to stretch will have a lower spring constant.
In short the spring constant characterizes the elastic properties of the spring in question. The spring force is the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it. An object that compresses or stretches a spring is always acted upon by a force that restores the object to its rest or equilibrium position.
A spring is an object that can be deformed by a force and then return to its original shape after the force is removed. Springs come in a huge variety of different forms but the simple metal coil spring is probably the most familiar. Each spring can be deformed stretched or compressed to some extent.
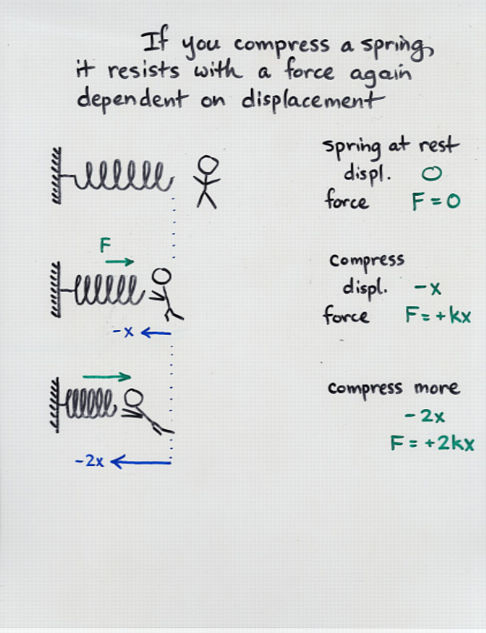
When the force that causes the deformation disappears the spring comes back to its initial shape provided the elastic limit was not exceeded. Hookes law states that for an elastic spring the force and displacement are proportional to each other. Spring Force Formula An object is in the periodic motion when its motion repeats with a defined cycle.
This type of motion is also oscillation. Simple examples are the movement of springs and pendulums but there are many other situations in which oscillations occur. Force spring force elastic force applied force deforming force.
You get the idea. Versions with subscripts are also common Fs Fe etc. Extension or compression of the spring.
That is the change in length from the springs relaxed natural or original length x0. The Spring Force Shows a spring in its relaxed state-that is neither compressed nor extended. One end is fixed and a particle-like object say a block is attached to the other free end.
If we stretch the spring by pulling the block to the right as the spring pulls on the block toward the left. Hookes law is a law of physics that states that the force F needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance x scales linearly with respect to that distancethat is Fs kx where k is a constant factor characteristic of the spring ie its stiffness and x is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The force exerted by a spring on objects attached to its ends is proportional to the springs change in length away from its equilibrium length and is always directed towards its equilibrium position.
Assume one end of a spring is fixed to a wall or ceiling and an object pulls or pushes on the other end. This video introduces the Spring Force as used in Physics. Hookes Law is given along with a few example problems.
The spring scale is measured in Newtons. This video shares the basics of how to use a spring scale. The spring scale is measured in Newtons.