Eventually it results in a new virus strain. Influenza A virus drift variants result from the positive selection of spontaneously arising mutants by neutralizing antibodies.
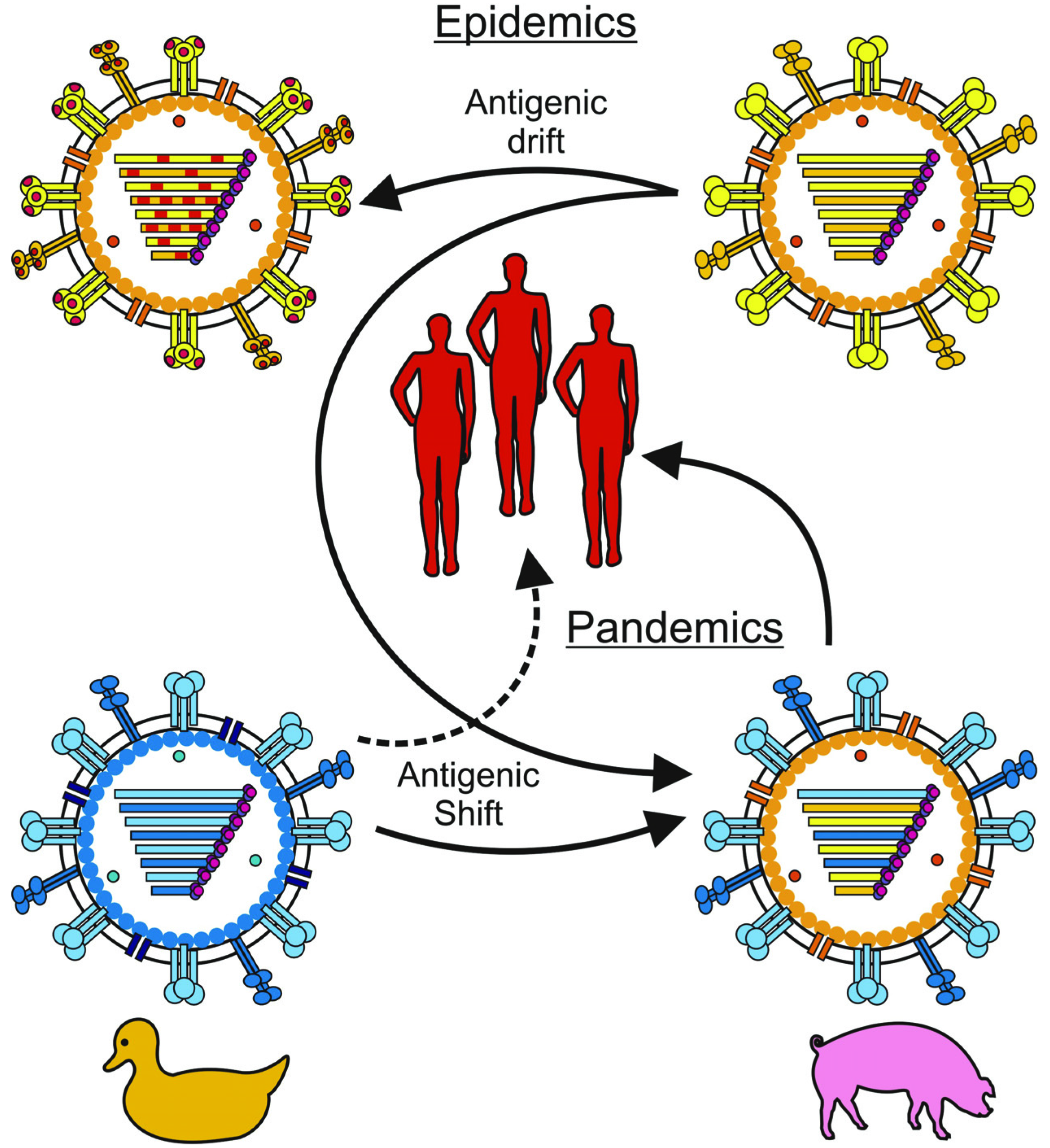
Similarly antigenic shift describes a similar phenomenon where two or more strains of different viruses combine to form a new virus.
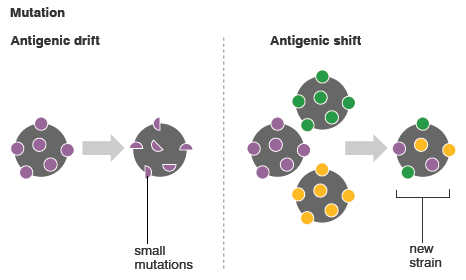
What is antigenic drift. Antigenic drift random genetic mutation of an infectious agent resulting in minor changes in proteins called antigens which stimulate the production of antibodies by the immune systems of humans and animals. These mutations typically produce antigens to which only part of a. One way influenza viruses change is called antigenic drift.
These are small changes or mutations in the genes of influenza viruses that can lead to changes in the surface proteins of the virus. HA hemagglutinin and NA neuraminidase. The HA and NA surface proteins of influenza viruses are antigens which means they are recognized by the immune system and are capable of triggering.
Antigenic drift relatively minor changes in the antigenic structure of a virus strain probably resulting from natural selection of variants circulating among an immune or partially immune population. See also antigenic shift. A minor change to a flu virus is known as antigenic drift.
Both influenza A and B viruses undergo antigenic drift. These mutations in the viruss genes can lead to changes in its surface proteins hemagglutinin HA and neuraminidase NA. A mechanism for variation by viruses that involves the accumulation of mutations within the antibody-binding sites so that the resulting viruses cannot be inhibited well by antibodies against previous strains making it easier for them to spread throughout a partially immune population.
This type of genetic mutation is called antigenic drift Influenza viruses can change through antigenic drift which is a process in which mutations to. Antigenic drift is a slow change in the viral genes occurring due to replication errors or random mutations. Eventually it results in a new virus strain.
Generally antigenic drift within genes coding for antigen-binding sites inhibits the effectiveness. Antigenic drift is a genetic variation which results from the gradual development of point mutations in the genes of H and N of the virus. Antigenic shift is a genetic variation which results from the genetic material exchange between two or more closely related strains of influenza virus.
Antigenic drift refers to the gradual accumulation of point mutations during annual circulation of influenza as a consequence of the high error rates associated with RNA-dependent RNA polymerase during virus replication. Influenza A virus mutants with antigenic changes tend to have a selective advantage over the nonmutant viral population. June 23 2018 by Sagar Aryal Influenza Virus are remarkable because of the frequent antigenic change that occurs in HA hemagglutinin or NA neuraminidase.
The two surface antigens of influenza undergo antigenic variation independent of. Antigenic drift describes a genetic variation in a virus that causes its antibodies or tags to change creating a new strain or form of the virus. Similarly antigenic shift describes a similar phenomenon where two or more strains of different viruses combine to form a new virus.
-What is the difference between antigenic drift and antigenic shift. Search for Influenza virus in text book Immunobiology of Janeway et al. 2001 two distinct ways of changing its antigenic type.
Influenza virus varies from year to year by a process of antigenic drift in. Antigenic shift is more concerning than antigenic drift. Antigenic shift can produce a version of influenza virus that no persons immune system has antibodies to protect against.
This is when an influenza pandemic can occur. Virtually everyone in the world is susceptible to the new virus. Antigenic shift is a specific case of reassortment or viral shift that confers a phenotypic change.
Antigenic shift is contrasted with antigenic drift which is the natural mutation over time of known strains of influenza or other things in a more general sense which may lead to a loss of immunity or in vaccine mismatch. Antigenic drift is the accidental alteration of genes encoding antigens. It typically occurs in viruses and enables the pathogen to evade the immune system triggering an infection once more.
Antigenic Drift Antigenic drift is caused by point mutations and is defined as the minor gradual antigenic changes in the HA or NA protein. Influenza A virus drift variants result from the positive selection of spontaneously arising mutants by neutralizing antibodies.