They are different from the human immunodeficiency viruses that cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. HTLV I and II Serology.
Therefore this study aims to assess the prevalence.
What is htlv 1 and 2. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus HTLV types 1 and 2 Overview. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus types 1 and 2 HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 are retroviruses found worldwide. HTLV-1 infects at least 5 million to 10 million people worldwide.
Synonyms of HTLV Type I and Type II acute T-cell leukemia acute T-cell lymphoma ATL HAMTSP HTLV-I associated myelopathy tropical spastic paraparesis. Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 HTLV-1 was the first discovered human retrovirus and the etiologic agent of adult T-cell leukemia and HTLV-1-associated myelopathytropical spastic paraparesis. Shortly after the discovery of HTLV-1 human T-cell leukemia virus type 2 HTLV-2 was isolated from a patient with hairy cell leukemia.
Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 HTLV-1 was the first discovered human retrovirus and the etiologic agent of adult T-cell leukemia and HTLV-1-associated myelopathytropical spastic paraparesis. Shortly after the discovery of HTLV-1 human T-cell leukemia virus type 2 HTLV-2 was isolated from a patient with hairy cell leukemia. Independent epidemiology for respective human T-cell lymphotropic virus HTLV types 1 and 2 is little known in blood donors in Brazil where screening for HTLV-12 is mandatory at blood banks but no testing to confirmdifferentiate these viruses.
Therefore this study aims to assess the prevalence. Das Typ-1-HTLV wurde zuerst aus T-Zell-Lymphomen isoliert an deren Entstehung es wohl maßgeblich beteiligt ist. Das HTLV Typ 2 kann eine Haarzell-Leukämie verursachen.
Das Typ-3-HTLV ist 2005 in Kamerum isoliert und beschrieben worden. HTLV-II wurde ebenfalls durch die Forschergruppe um Robert Gallo entdeckt. Welche Rolle das Virus bei der Entstehung menschlicher Krankheiten spielt ist bis heute nicht geklärt.
Die Zahl der Infizierten ist zudem deutlich geringer als bei HTLV-1 weshalb diesem Virustyp eine geringere Bedeutung beigemessen wird. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 HTLV-1 is a retroviral infection that affect the T cells a type of white blood cell. Although this virus generally causes no signs or symptoms some affected people may later develop adult T-cell leukemia ATL HTLV-1 associated myelopathytropical spastic paraparesis HAMTSP or other medical conditions.
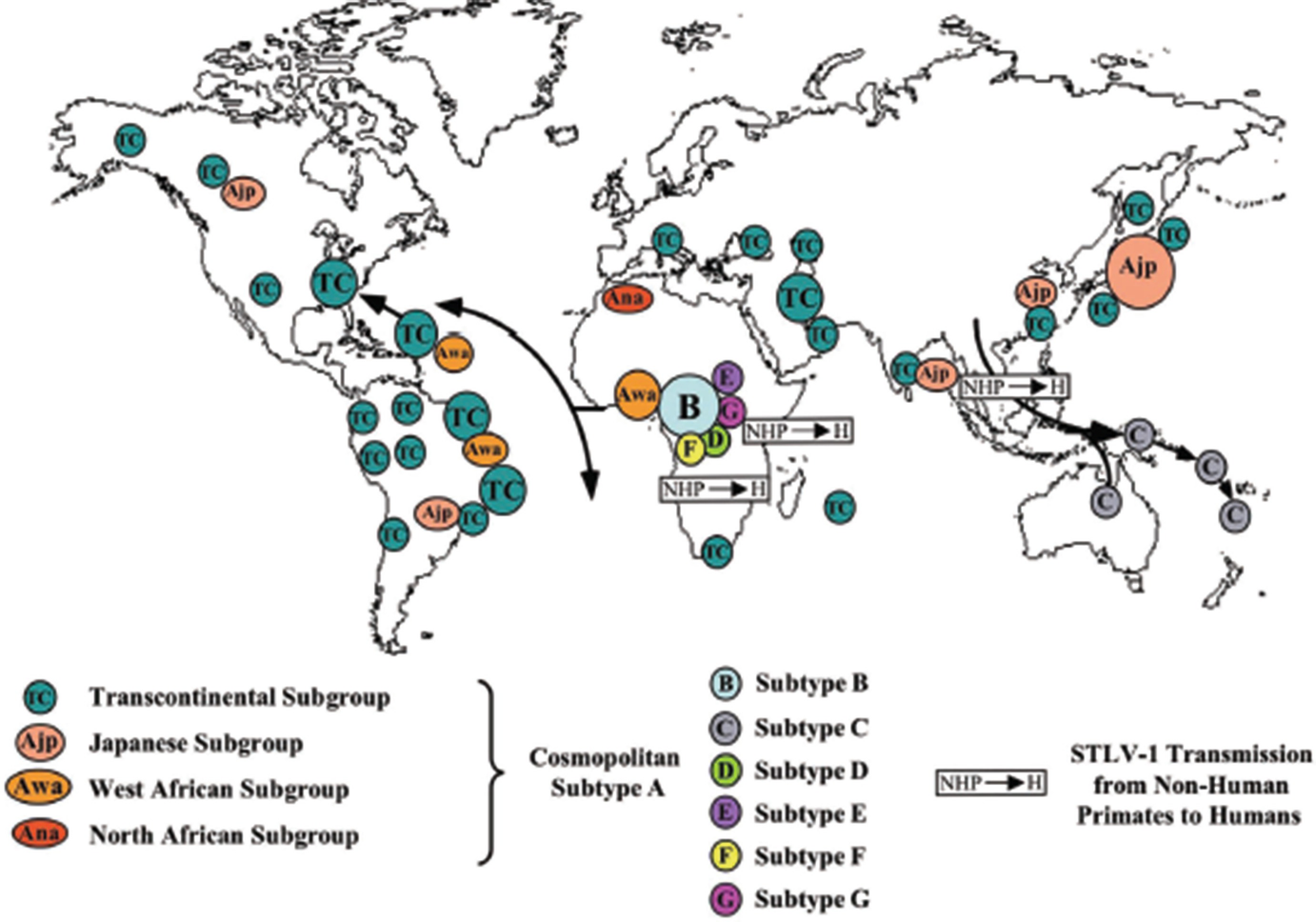
HTLV infection is concentrated in specific areas of Japan Central and South Africa the Caribbean and Latin America. Among indigenous populations in Latin America HTLV-1 infection has been reported in groups living in the Andean highlands whereas HTLV-2 has been reported in groups living in the lowlands. 1 3 Although several Latin American countries have reported the presence of HTLV.
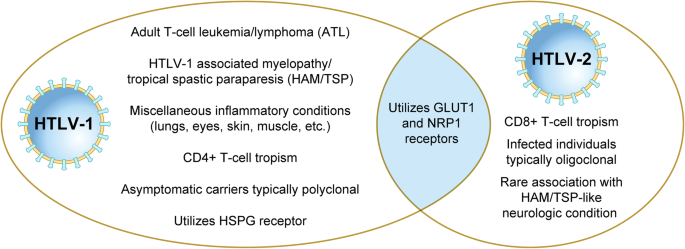
The human T-lymphotropic viruses type I HTLV-I and type II HTLV-II are closely related but distinct retroviruses that can infect humans. They are different from the human immunodeficiency viruses that cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus types I and II HTLV-I and HTLV-II are closely related exogenous human retroviruses.
HTLV-I was first isolated in 1980 from a patient with a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma while HTLV-II was identified from a patient with hairy cell leukemia in 1982. HTLV-2 binds and enters cells through GLUT-1 and NRP1 but not HSPGs. Both viruses infect T lymphocytes but B lymphocytes and dendritic cells can also be involved.
T-cell tropism is differs between HTLV-I and II. Although HTLV-I preferentially infects activated CD4 T lymphocytes HTLV-II infects CD8 T lymphocytes. HTLV I and II Serology.
Valid only on day of print. Specimen Collection and Handling Requisitions and Kit Ordering Test Frequency and Turnaround Time TAT Reporting Test Methods Labstracts. Specimen Collection and Handling Requisitions and Kit Ordering Test Frequency and Turnaround Time TAT Reporting Test.