This review discusses the structure function and formation of kinetochore fibers and interpolar bundles with an emphasis on how they interact. Two centrosomes have formed.

Identical joined copies of a single chromosome are known as sister chromatids.
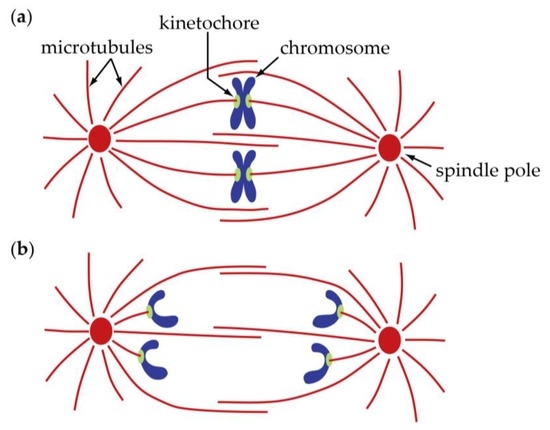
What is kinetochore fibers. Microtubules that bind a chromosome are called kinetochore microtubules. Kinetochore fibers extend from the kinetochore region and attach chromosomes to microtubule spindle polar fibers. These fibers work together to separate chromosomes during cell.
A kinetochore is a protein structure that forms on a chromatid during cell division and allows it to attach to a spindle fiber on a chromosome. A kinetochore is a protein structure that forms on a chromatid during cell division and allows it to attach to a spindle fiber on a chromosome. During the replication process the two chromatids unite by way of a centromere or the part of the chromosome that is connected to the spindle fiber.
Kinetochore fibers hold on tight to interpolar bundles Abstract. When a cell starts to divide it forms a spindle a micro-machine made of microtubules which separates the. Cell division is one of the most fundamental processes in the living world.
At the onset of. This review discusses the structure function and formation of kinetochore fibers and interpolar bundles with an emphasis on how they interact. Their connections have an impact on the force balance in the spindle and on chromosome movement during mitosis because the forces in interpolar bundles are transmitted to kinetochore fibers and hence to kinetochores through these connections.
The kinetochore is a structure in a cells nucleus that is involved in mitosis and meiosis the two processes of cell division. Kinetochores are specialized regions located on the centromeres of chromosomes and they are made up of many types of proteins. Together our data reveal that kinetochore-driven K-fiber formation is a major mechanism that contributes toward spindle assembly during normal mitosis in centrosomal cells.
However integration of these kinetochore-organized K-fibers into the common spindle is facilitated by the centrosomes via a dynein-dependent search-and-capture. Identical joined copies of a single chromosome are known as sister chromatids. The centromere is also where protein complexes called kinetochores are found.
Kinetochores generate fibers that attach sister chromatids to spindle fibers. Kinetochore fibers and spindle polar fibers work together to separate chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. The vertebrate kinetochore is a complex structure that specifies the attachments between the chromosomes and microtubules of the spindle and is thus essential for accurate chromosome segregation.
Kinetochores are assembled on centromeric chromatin through complex pathways that are coordinated with the cell cycle. A kinetochore is a protein complex assembled on centromeres of chromosomes. Centromeres can be observed under the light microscope.
Kinetochores are only visible under the electron microscope. Centromeres consist of centric heterochromatin. Kinetochore-driven outgrowth of microtubules is a central contributor to kinetochore fiber maturation in crane-fly spermatocytes.
Living cells and dynamic molecules observed with the polarized light microscope. The legacy of Shinya Inoue. What is Kinetochore.
Kinetochore is a disc-shaped protein complex present in the centromere region of a chromosome which is in the mitotic or meiotic division. Each chromosome has a kinetochore. The functions of these complexes are to bind microtubules of the spindle bundle and depolarize them during the cell division.
At cell division the mammalian kinetochore binds many spindle microtubules that make up the kinetochore-fiber. To segregate chromosomes the kinetochore-fiber must be dynamic and generate and respond to force. Yet how it remodels under force remains poorly.
Chromosomes are attached to kinetochore microtubules via a multiprotein complex called the kinetochore. Polar microtubules interdigitate at the spindle midzone and push the spindle poles apart via motor proteins. Astral microtubules anchor the spindle poles to the cell membrane.
A kinetochore is where the spindle fibers attach to the chromosome. What happens in G2 of interphase. The nuclear envelope is still present.
Two centrosomes have formed. Chromosomes were duplicated in S phase have not yet condensed in the cell. What happens in prophase.
Kinetochore fibers are the main generators of forces that move the chromosomes during mitosis. During anaphase kinetochore fibers shorten by depolymerization at the kinetochore and at the pole thereby segregating sister chromatids towards the opposite spindle poles Asbury 2017. Find an answer to your question What are kinetochore fibers.
Honeydrall8411 honeydrall8411 11122018 Biology Secondary School 25 pts. Answered What are kinetochore fibers. So spindle fibers are on the centriole.
Kinetochores are on the centromere. Spindle fibers do the attaching of the centriole to the chromosome but the kinetochore makes binding of the spindle fibers to the chromosome possible. Hope that made sense.