It is actively secreted through the B. Clinical expression ranges from asymptomatic infection in children.
During a bacterial infection the toxin is secreted and causes inflammation of the respiratory tract which interferes with the clearing of pulmonary secretions.
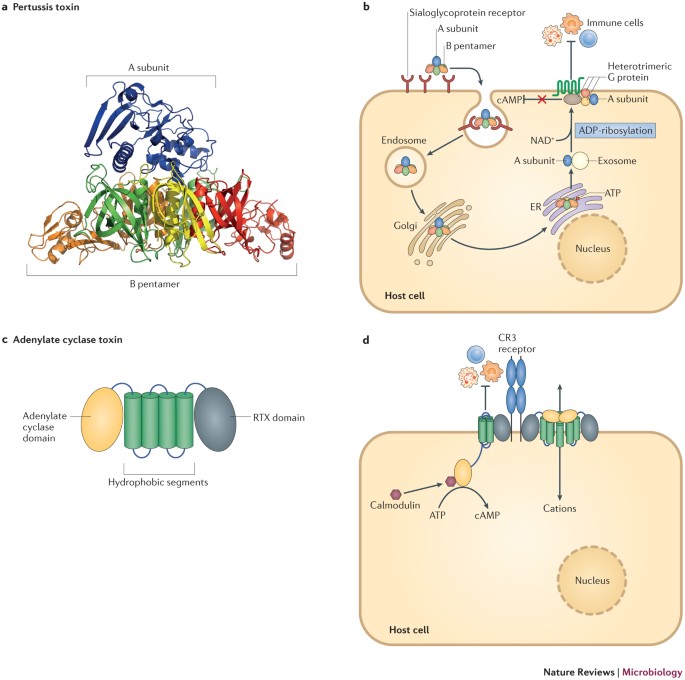
What is pertussis toxin. Pertussis toxin previously termed lymphocytosis-promoting factor is a major contributor to the pathogenesis of pertussis and is generally believed to play an important role in the induction of clinical immunity. PT is an oligomeric structure composed of five different subunits S1 through S5 figure 23-1. Structurally it belongs to the A-B class of bacterial toxins.
The S1 component A. Pertussis toxin produced and secreted by the whooping cough agent Bordetella pertussis is one of the most complex soluble bacterial proteins. It is actively secreted through the B.
Pertussis cell envelope by the Ptl secretion system a member of the widespread type IV secretion systems. Pertussis toxin PT is a protein-based AB 5 -type exotoxin produced by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. PT is involved in the colonization of the respiratory tract and the establishment of infection.
Pertussis toxin PT is a biological toxin that is secreted from the bacterium Bordetella pertussis which is the causative agent of whooping cough. During a bacterial infection the toxin is secreted and causes inflammation of the respiratory tract which interferes with the clearing of pulmonary secretions. The toxin appears to.
Pertussis-Toxin Keuchhusten-Toxin ein von Bordetella pertussis gebildetes aus einer bindenden und einer funktionellen Untereinheit aufgebautes Protein. Die bindende Untereinheit lagert sich an den Rezeptor der eukaryontischen Zelle an während die funktionelle Untereinheit ein inhibitorisches G-Protein ADP-ribosyliert ADP-Ribosylierung wodurch die Inaktivierung der Adenylat-Cyclase. Dem Pertussis-Toxin PTx PTx ist ein Exotoxin das sowohl zellgebunden als auch in der extrazellulären Flüssigkeit vorkommt.
Das Polypeptid besteht aus einer A- und einer B-Komponente. Pertussis toxinPertussis toxin subunit 1The Crystal Structure of Pertussis Toxin1IdentifiersSymbolPertussis_S1PfamPF02917InterProIPR003898SCOP1bcpSUPERFAMILY1bcp. Pertussis vaccine is a vaccine that protects against whooping cough.
There are two main types. Whole-cell vaccines and acellular vaccines. The whole-cell vaccine is about 78 effective while the acellular vaccine is 7185 effective.
The effectiveness of the vaccines appears to decrease by between 2 and 10 per year after vaccination with a more rapid decrease with the acellular vaccines. Pertussis toxin PTX produced by Bordetella pertussis was first introduced by Ui and his colleagues in research on signal transduction under the name islet-activating protein in 1979 when the mechanism of toxin-induced stimulation of insulin release from pancreatic islets was reported in the rat. The stimulatory effect of PTX in vivo results from the blockage of α2-adrenergic receptor-mediated inhibition of.
Bordetella pertussis a gram-negative bacterial pathogen of the human respiratory tract secretes at least two protein toxins pertussis toxin PT and adenylate cyclase toxin ACT that are important virulence factors in mouse models of infection. Pertussis whooping cough is caused by Bordetella pertussis a small Gram-negative coccobacillus that infects the mucosal layers of the human respiratory tractIt is transmitted from infected to susceptible individuals through respiratory droplets. After an incubation phase of 7-10 days patients develop nose and throat inflammation and cough and in the course of 1-2 weeks coughing spasms.
Bordetella pertussis is a Gram-negative aerobic pathogenic encapsulated coccobacillus of the genus Bordetella and the causative agent of pertussis or whooping cough. Pertussis is motile and expresses a flagellum-like structure. Its virulence factors include pertussis toxin adenylate cyclase toxin filamentous hæmagglutinin pertactin fimbria and tracheal.
Pertussis-Toxin Keuchhusten-Toxin ein aus einer funktionellen und einer bindenden Untereinheit aufgebautes Protein das von Bordetella pertussis gebildet. Pertussis produces a range of virulence factors including pertussis toxin and pertactin which cause the typical disease symptoms. The clinical spectrum is diverse and is affected by patient age previous exposure to the organism immunisation history antibiotic administration and concomitant infections with other agents.
Clinical expression ranges from asymptomatic infection in children.