Propane C 3 H 8 370. Every substance has a critical temperature.
The transition between a liquidgas mixture and a supercritical phase is demonstrated for a sample of benzene in Figure PageIndex1.
What is the critical pressure of water. At pressure that is higher than the critical pressure of water water is in special state that is known as supercritical fluid state. Critical pressure is Pcr 2209 MPa. At pressure that is higher than the critical pressure of water water is in special state that is known as supercritical fluid state.
Critical pressure is Pcr 2209 MPa. Critical Point of Water. In thermodynamics a critical point or critical state is the end point of a phase equilibrium curve.
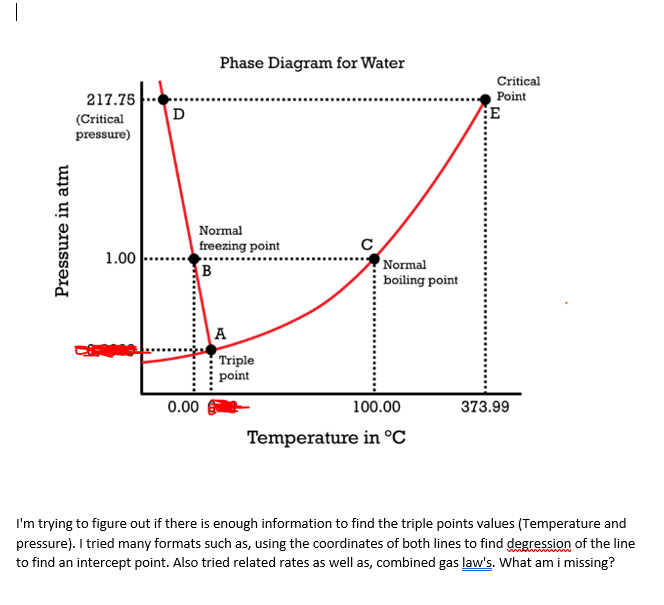
The phase diagram of water is a pressure-temperature diagram for water that shows how all three phases solid liquid and vapor may coexist together in thermal equilibrium. The critical pressure of water is 3206 psia. Boilers in conventional power plants have utilized once-through supercritical steam cycles since the mid-1950s.
Once-through designs are more appropriate for supercritical operation because there is no phase change from water to. Note that at or above 374oC the critical temperature for water only water vapor exists in the tube. What is the critical pressure of water.
- 3048794 dexterassault15 dexterassault15 17092020 Science Senior High School answered What is the critical pressure of water. For water the critical pressure is very high 21775 atm. The critical point is the intersection point of the critical temperature and the critical pressure.
Every substance has a critical temperature. The pressure required to liquify a substance vapor at its critical temperature. The end point of the pressure-temperature curve that designates conditions under which a liquid and its vapor can coexist.
At higher temperatures the gas cannot be liquefied by pressure alone. At the critical point defined by the critical temperature T. At pressures above the critical pressure properties of water in the reactor change gradually and continuously from those we ordinarily associate with a liquid high density small compressibility to those of a gas low density large compressibility without a phase change.
There is no change in the phase of water in the core. On the other hand physical properties such as density. For a pure substance the critical pressure is defined as the pressure above which liquid and gas cannot coexist at any temperature.
The critical temperature for a pure substance is the temperature above which the gas cannot become liquid regardless of the applied pressure. Critical point is where vapor and liquid are indistinguishable and triple point is where ice water and vapor coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium Water vapor pressure of 21775 atm 22064 bar 22064 MPa 32001 psi Temperature of 647096 K 373946 C 705103 F Critical point density. For example the density of water at its critical point T 374C P 2177 atm is 032 gmL about one-third that of liquid water at room temperature but much greater than that of water vapor under most conditions.
The transition between a liquidgas mixture and a supercritical phase is demonstrated for a sample of benzene in Figure PageIndex1. At the critical temperature the. Critical pressure is the pressure below which it is not possible to carry out condensation of gas at a critical temperature.
Critical pressure is specific for a given substance. For example the critical pressure of hydrogen H 2 is approximately 13 MPa ie. Critical pressure and temperature of water are 220 bar and 37314 C as steam water is a valuable heating agent below 200 C where the saturation pressure is about 24 bar.
Superheated steam can be used above the saturation limit. The vapour pressure of water is the pressure at which water vapour is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed stateAt higher pressures water would condenseThe water vapour pressure is the partial pressure of water vapour in any gas mixture in equilibrium with solid or liquid water. As for other substances water vapour pressure is a function of temperature and can be determined with.
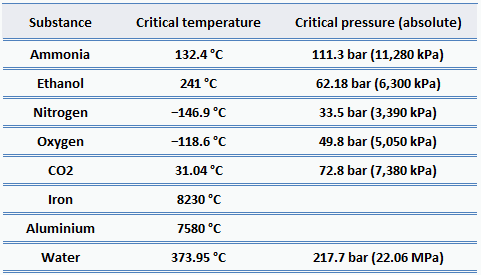
Critical Pressures of Some Common Substances The critical pressure of water corresponds to 2177 atm or 22060 kiloPascals. The critical pressure of ammonia chemical formula. NH 3 corresponds to 1113 atm or 11280 kiloPascals.
The critical pressure of chlorine symbol. Cl corresponds to 76 atm. Critical Temperature K Critical Pressure MPa Critical Pressure atm Hydrogen H 332.
Carbon dioxide CO 2 3042. Propane C 3 H 8 370. Ammonia NH 3 4055.