
Ecological systems theory is a theoretical framework for understanding the organization of living and non-living components in an ecosystem. The ecosystems perspective in social work emerged in the 1970s from two bodies of scientific theory General Systems Theory and ecological theory.
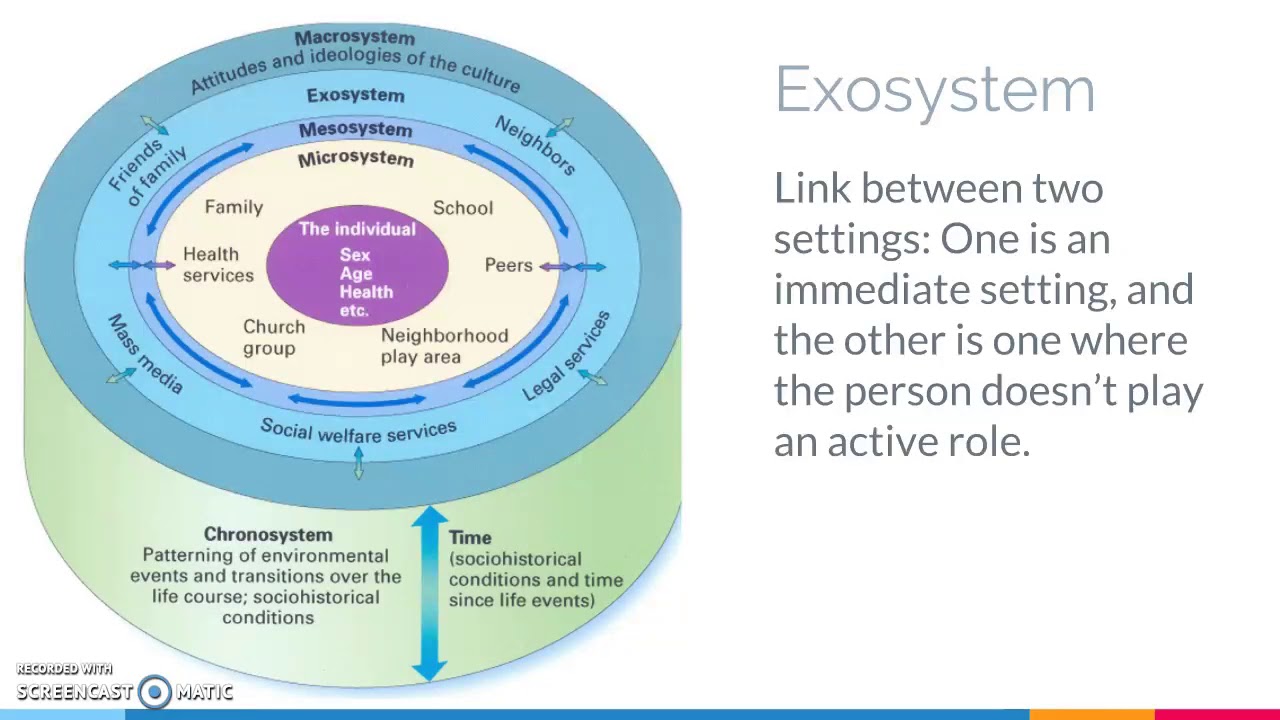
The ecosystems perspective in social work emerged in the 1970s from two bodies of scientific theory General Systems Theory and ecological theory.
What is the ecosystem theory. Ecosystems theory was derived from early sociologists who compared society to a living orgainism. It attempts to apply an ecological perspective to. Ecological systems theory deals with ways in which a childs development is impacted by environmental factors such as interaction with parents.
The ecological systems theory which is also known as development in context is a developmental theory that serves to explain how a childs environment affects how he or she develops. Systems theories help us to think about these interactions between people and their social and physical environments and they help us to understand how change can occur through the use of ecosystem interventions. In chapter 1 we talked about how social work theory helps us to explain human experience and how people and their environments change.
The ecosystems theory is a combination of ecology and general systems theory. According to the American Heritage Dictionary ecology is The science of the relationship between organisms and their environments Bantam Dell 2007 p. The ecosystems perspective in social work emerged in the 1970s from two bodies of scientific theory General Systems Theory and ecological theory.
The available research suggests that social. Ecosystem theory is built up by a hierarchical set of comprehensive ecological hypotheses which have to be integrated into an abstract system of coherent contexts and principles. Ecological systems theory is a theoretical framework for understanding the organization of living and non-living components in an ecosystem.
Ecological systems theory is a holistic approach to understanding the natural world. Ecosystem leadership and Theory U is about letting go of old patterns of thought and action and operating from a place of curiosity compassion and courage. It requires leading from the edges.
An ecosystem consists of the biological community that occurs in some locale and the physical and chemical factors There are many examples of ecosystems – a pond a forest an estuary a grassland. The boundaries are not fixed in any objective way although sometimes they seem obvious as with the shoreline of a small pond. The term ecological perspective is a concept from the science of ecology that refers the study of organisms and how they interact with their environments.
The ecosystems theory of social work encourages those in the field to look at the environment surrounding a person or group when attempting to provide support. Click to see full answer. Ecosystems we posit are interacting organizations enabled by modularity not hierarchically managed bound together by the nonredeployability of.
So no matter what theories the ecosystem approach is based on the idea behind this concept is a wide range of interconnections. Every smaller object such as a person is part of a large range of interactions of larger systems. Family community society environment and so on.
With the environment folded in those principles fail to be explanatory. In the ecosystem concept flows of material and energy come to the fore. Connection and flux are the hallmark of ecosystems.
In ecosystems animals melt away into pathways and become a connection between food eaten and waste expelled. Animals become connectors between vegetation and the soil. Product ecosystem theory is an emerging theory that describes how the design of manufactured products evolves over time and draws parallels with how species evolve within a.
Ecological model and systems theory You reach Dr. The ecological model rests on an evolutionary adaptive view of human beings in continuous interaction with their environment. In biology accommodation occurs when an individual actively interacts with their environment to ensure a goodness-of-fit Germaine 1979.