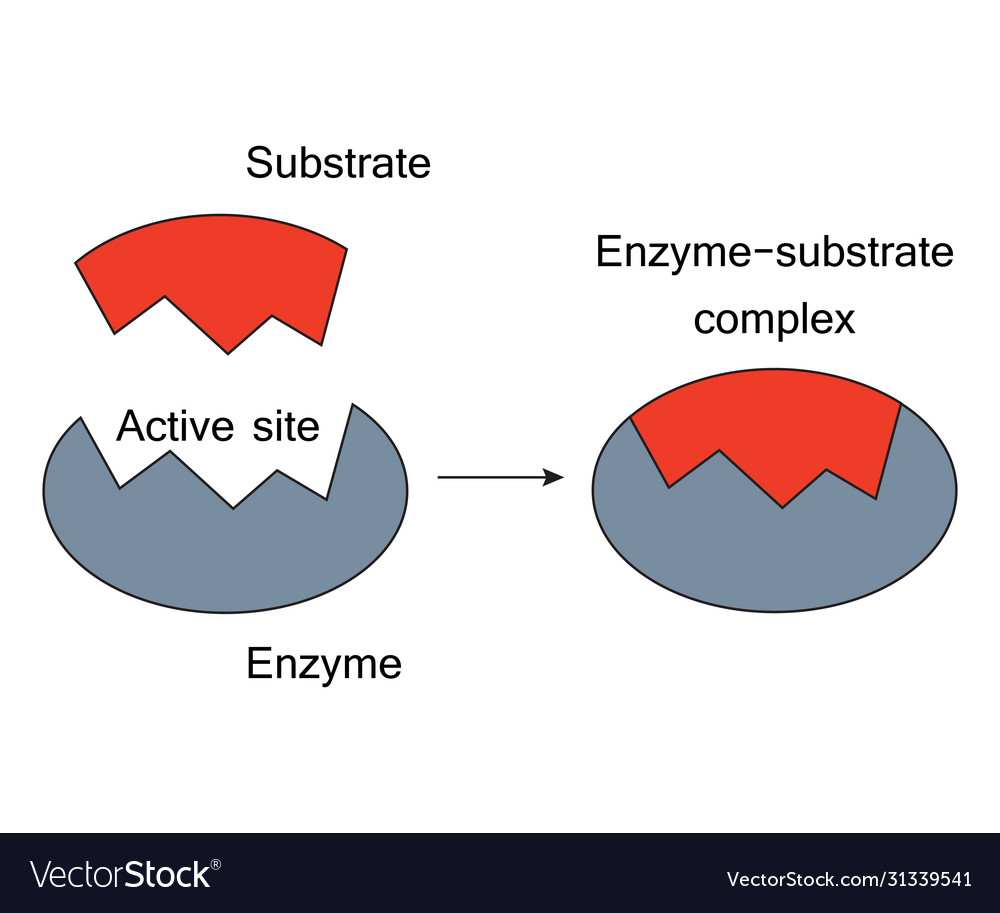
In the case of a single substrate the substrate bonds with the enzyme active site and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. In our saliva is an enzyme.

Also what is the substrate for horseradish peroxidase.
What is the substrate of an enzyme. Enzyme Substrate Complex Enzyme Substrate Complex Definition. The enzyme substrate complex is a temporary molecule formed when an enzyme comes. Examples of Enzyme Substrate Complex.
Amylose is a complex sugar produced by plants. In our saliva is an enzyme. The enzyme substrate complex is a temporary molecule formed when an enzyme comes into perfect contact with its substrate.
Without its substrate an enzyme is a slightly different shape. The substrate causes a conformational change or shape change when the substrate enters the active site. The active site is the area of the enzyme capable of forming weak bonds with the substrate.
Enzymes are substances that play a crucial role in carrying out biochemical reactions. Chemically they are proteinaceous in nature which act on substrates to give the end result of the reactions called products. When a substrate binds to a specific enzyme it is called an enzyme-substrate complex.
In biochemistry the substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrates. In the case of a single substrate the substrate bonds with the enzyme active site and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed.
Specificity is the ability of an enzyme to choose exact substrate from a group of similar chemical molecules. The specificity is actually a molecular recognition mechanism and it operates through the structural and conformational complementarity between enzyme and substrate. Enzymes show different degrees of specificity towards their substrate.
Each enzyme has an active site which is where one of the substrate molecules can bind to. Thus an enzyme- substrate complex is formed. This enzyme-substrate molecule now reacts with the second substrate to form the product and the enzyme is liberated as the second product.
There are many theories that explain how enzymes work. But there are two important theories that. Food or food enzymes are all those enzymes found in foods of animal or plant origin such as lipase cellulase protease and amylase.
These types of enzymes have active units that favor the process of decomposition of proteins fats and carbohydrates in the body. Beside this what is the substrate of the enzyme peroxidase How do you know. Hydrogen peroxide is the substrate of the enzyme peroxidase.
It is due to the fact that any chemical reactions that involve hydrogen peroxide are able to be catalyzed by peroxidase. Also what is the substrate for horseradish peroxidase. M is also the substrate concentration at which the enzyme operates at one half of its maximum velocity K M S at ½ V max -Understanding K m the Michaelis Constant K M is the Michaelis constant K M is constant for any given enzymesubstrate pair Independent of substrate or enzyme concentration units are in terms of concentration.
Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrates. In the case of a single substrate the substrate bonds with the enzyme active site and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. What are three enzymes and their substrates.
Examples of specific enzymes. Lipases a group of enzymes that help digest fats in the gut. A substrate is substance on which enzymes acts to covert into a product.
For many enzymes there is only one specific substrate. But most enzymes have two or more substrates. A substrate is very specific for an enzyme to catalyze the reaction.
In the induced-fit theory of enzyme-substrate binding a substrate approaches the surface of an enzyme step 1 in box A B C and causes a change in the enzyme shape that results in the correct alignment of the catalytic groups triangles A and B. Circles C and D represent substrate-binding groups on the enzyme that are essential for catalytic. A reactant in a chemical reaction is called a substrate when acted upon by an enzyme.
Proposes that the initial interaction between enzyme and substrate is relatively weak but that these weak interactions rapidly induce conformational changes in the enzyme that strengthen binding. The enzyme acts are called substrates. Enzymes operate in tightly organized metabolic systems called pathways.
Enzymes ˈɛnzaɪmz are proteins that act as biological catalysts biocatalysts. Catalysts accelerate chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products.
Creative Enzymes offers substrate screening and identification service which is an important step for all enzyme related research. For novel enzymes or enzymatic reactions we are able to quickly develop protocols for substrates screening including determining the natural substrate of an enzyme. Libraries including 10000 substrates Categorized by function and structure similarity Metabolic.